F Waves Ekg

Causes Of Cardiac Arrhythmias Ppt Video Online Download
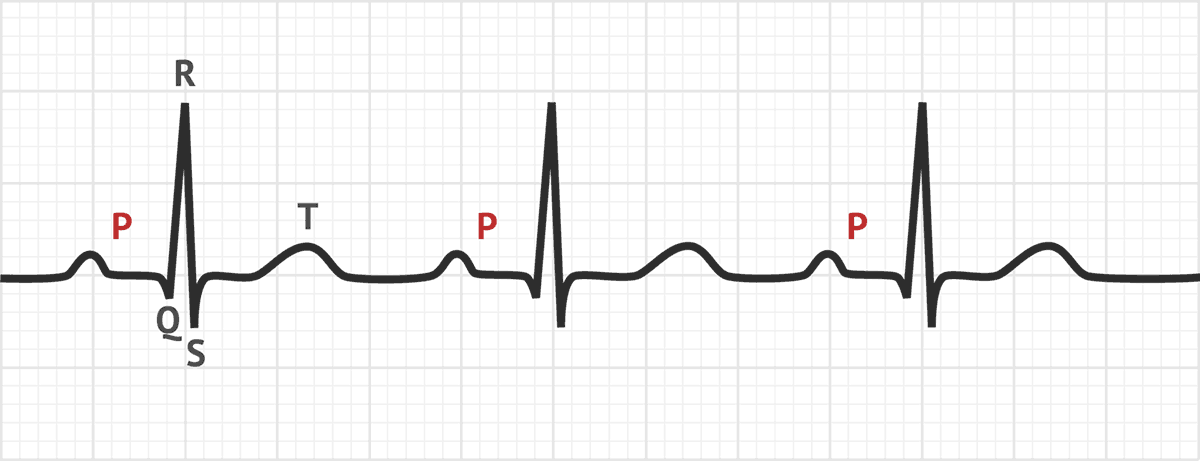
The P Wave Ecg Basics Medschool
Q Tbn 3aand9gcqd5hwdwpwg5ur3ji Zbas6f3i7 0qjfamk Gqtspz Fl9sddo Usqp Cau
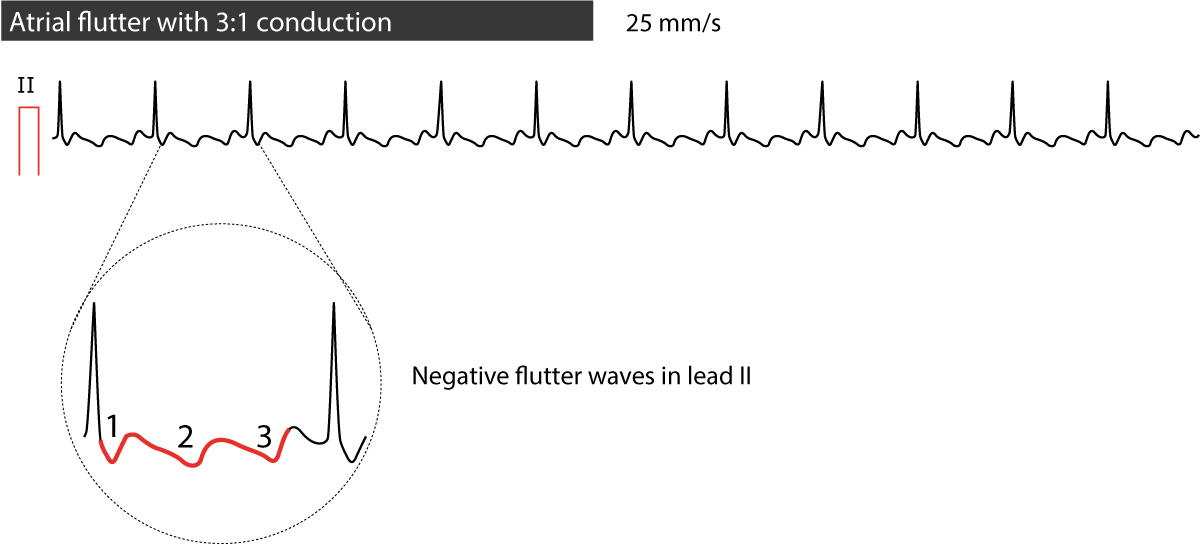
Atrial Flutter Classification Causes Ecg Diagnosis Management Ecg Echo
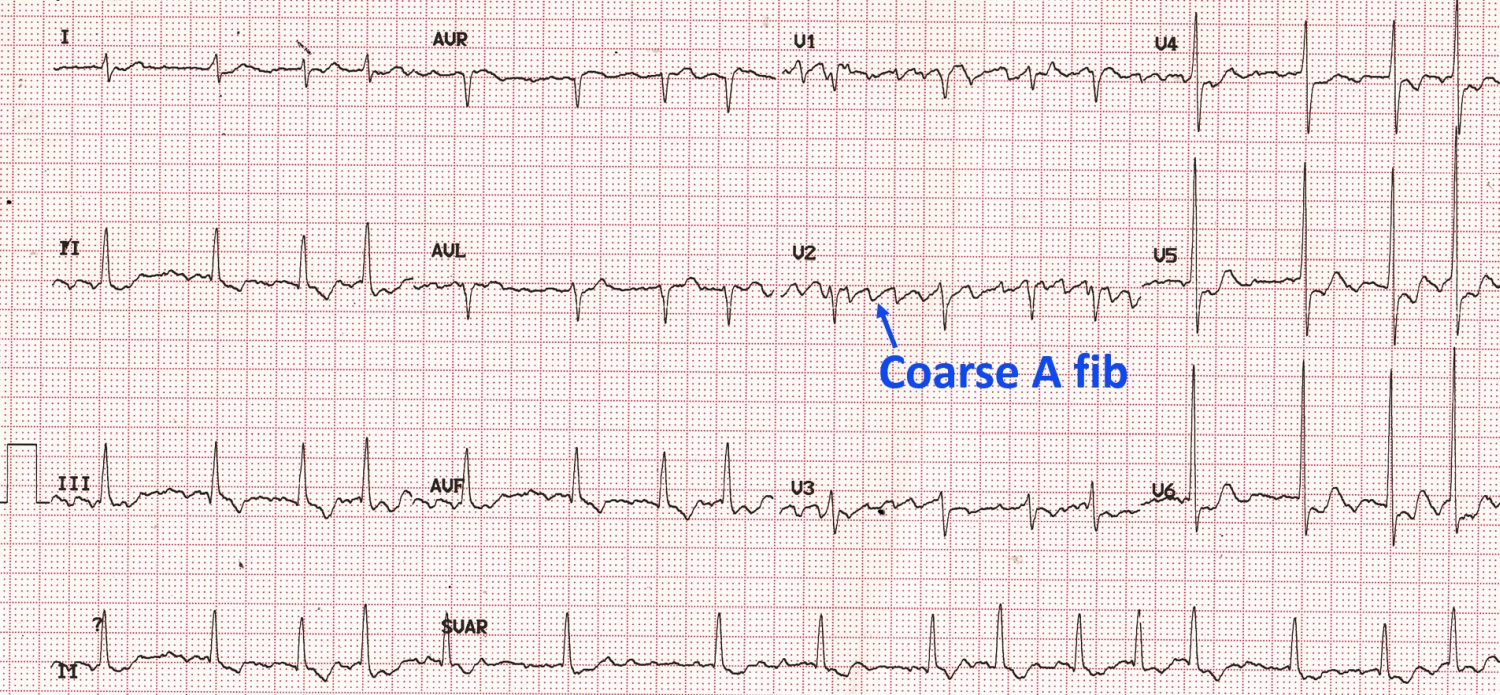
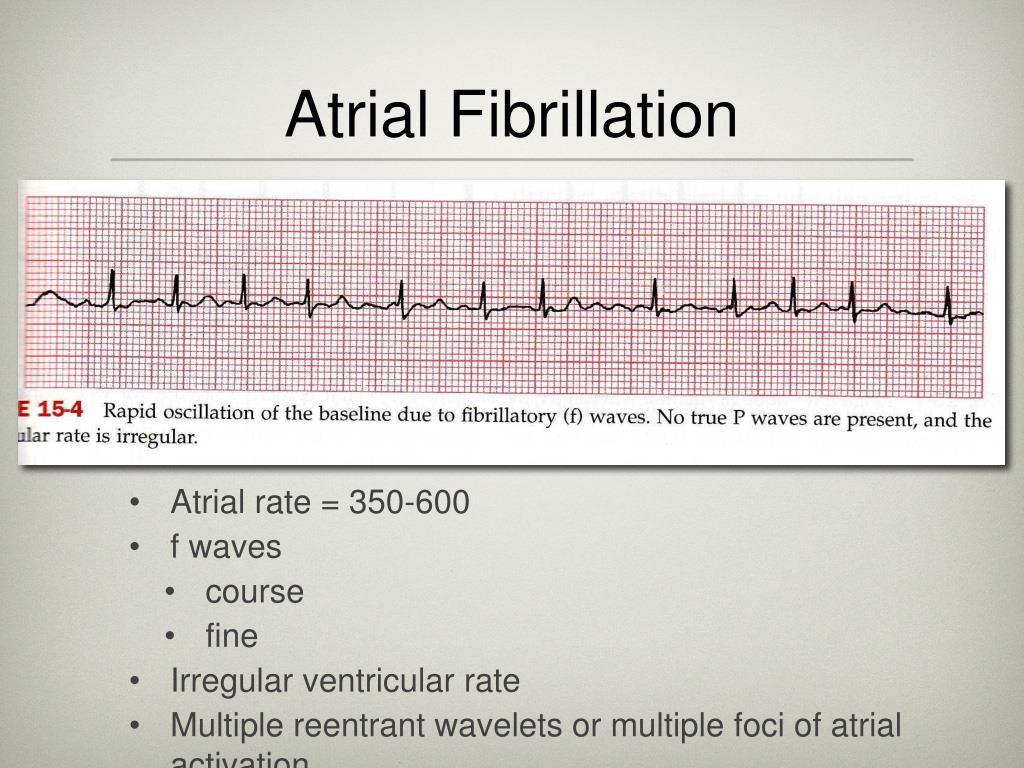
Coarse Atrial Fibrillation On Ecg All About Cardiovascular System And Disorders

Separating Atrial Flutter From Atrial Fibrillation With Apparent Electrocardiographic Organization Using Dominant And Narrow F Wave Spectra Sciencedirect
It means looking great while doing it.
F waves ekg. A Q wave is any negative deflection that precedes an R wave. This chaotic electrical activity results in a chaotic wave form between the QRS complexes. And then a downwards S wave.
Note the 'Flutter' or 'F' waves. Representing ventricular repolarization, T waves are located after the QRS complex on an EKG. As part of the QRS complex, an R wave is an important indicator of cardiac health.
The ECG findings of a pathologic Q wave include a Q wave duration of > 40 milliseconds (one small box) or size > 25% of the QRS complex amplitude. Lead III often shows Q waves, which are not pathologic as long as Q waves are absent in leads II and aVF (the contiguous leads). The signals are shown as waves on an attached computer monitor or printer.
In neuroscience, an F wave is one of several motor responses which may follow the direct motor response evoked by electrical stimulation of peripheral motor or mixed nerves. And without the drawbacks and costly upkeep of asphalt shingles, natural wood shingles, and real slate roofing tiles. The F-waves of flutter can take a variety of morphologies, but most often the bulk of the wave is negative in the inferior leads and upright in V1.
Anthony Kashou (The EKG Guy) is a physician resident at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota. The normal U wave is asymmetric with the ascending limb moving more rapidly than the descending limb (just the opposite of the normal T wave). Aldose reductase inhibition ameliorates pupillary light reflex and F-wave latency in patients with mild diabetic neuropathy.
The P wave should be upright in lead II if the action potential is originating from the SA node. See detailed information below for a list of 4 causes of Absent P waves on ECG, Symptom Checker, including diseases and drug side effect causes. U waves are usually best seen in the right precordial leads especially V2 and V3.
The ECG shows regular flutter waves (F-waves;. Associated leg pain occurs less frequently. Am J Emerg Med.
Absence of pathologic Q waves does not exclude a myocardial infarction!. Create the best shingle the world has ever seen. If we move along the graph of the ECG, we see a small dip followed by a large spike and another dip.
An electrocardiogram (ECG) may be requested as part of the investigation of a wide range of problems in paediatrics, often in patients who have no clinical evidence of cardiac disease. (2)Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee, USA. The ECG is recorded at a speed of 25 mm/sec (5 large squares/sec), and the voltages are calibrated so that 1 mV = 10 mm (2 large squares) in the vertical direction.
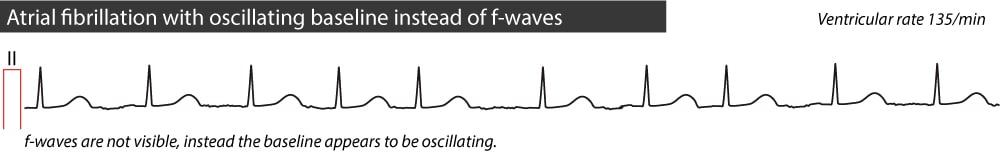
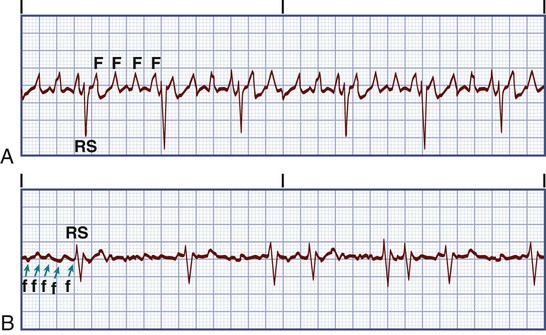
The amplitude of f wave arises along with the deepening of the catheter tip. (A lowercase f indicates atrial fibrillation). What do "slightly flat" s/t waves mean on a routine ekg?.
1st negative deflection of QRS complex after P wave or before 1st R wave ;. Less commonly, F waves are undulating, firing at a rate of 280-3/min, a rate often associated with a 2:1 block and alternating F waves merge with QRS or T waves Neurology. The f wave is modified by the near field potential and the far field potential.
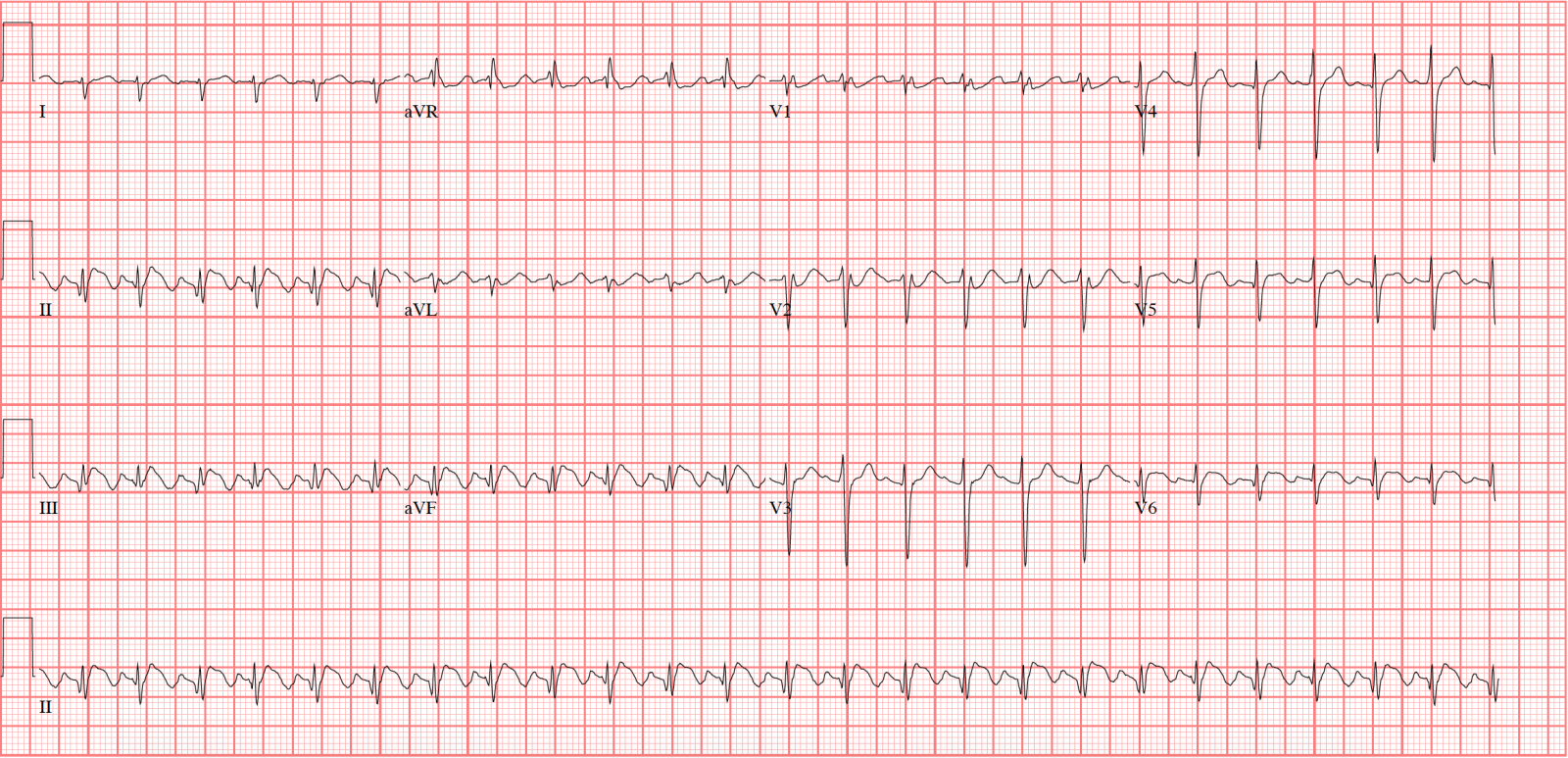
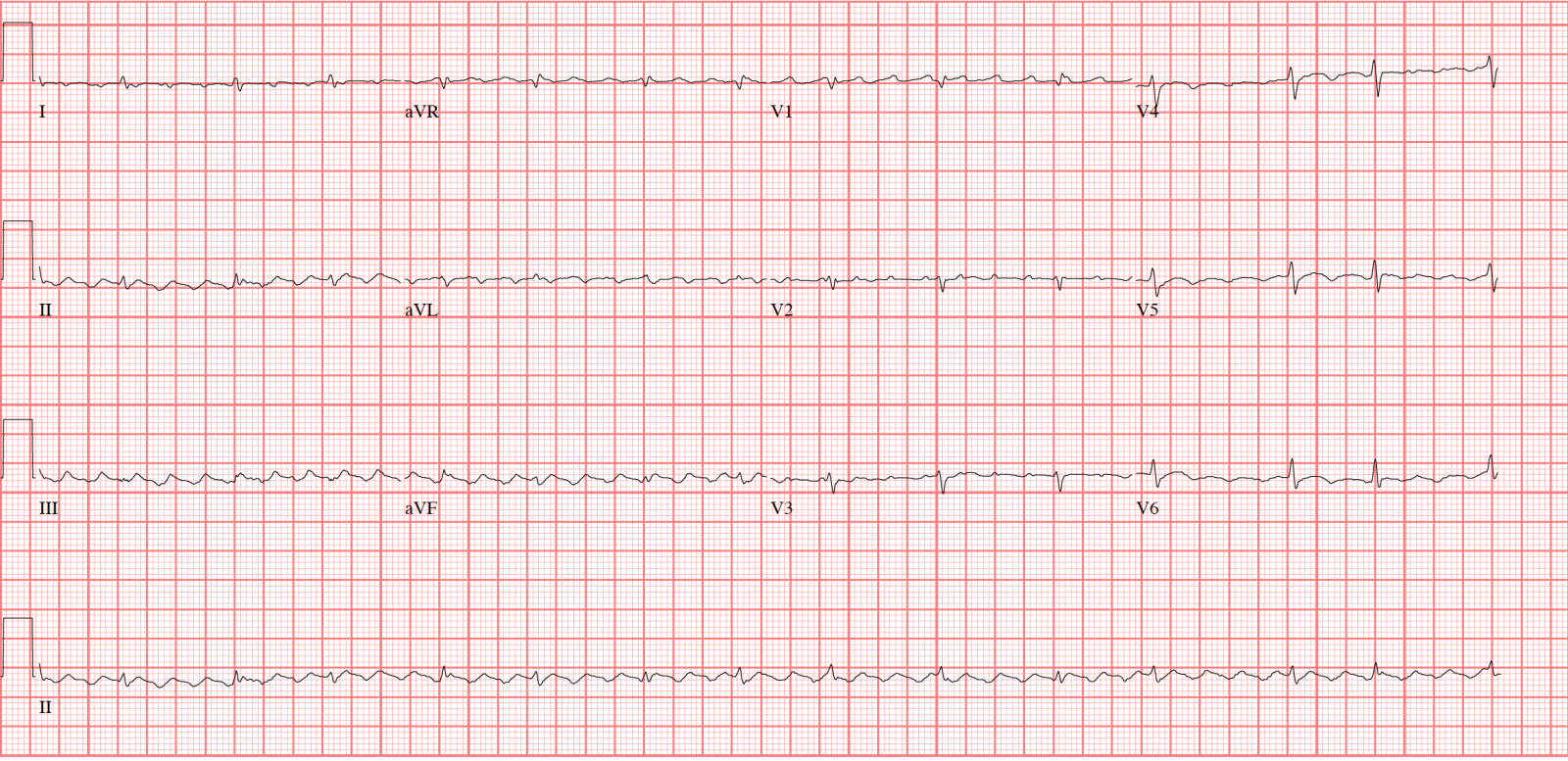
Approximately 80% of the population is plagued at one time or another by back pain. Inverted T waves are normal in children, and they sometimes remain inverted into adulthood. Atrial flutter is the only diagnosis causing this baseline appearance, which is why it must be recognized on the ECG.
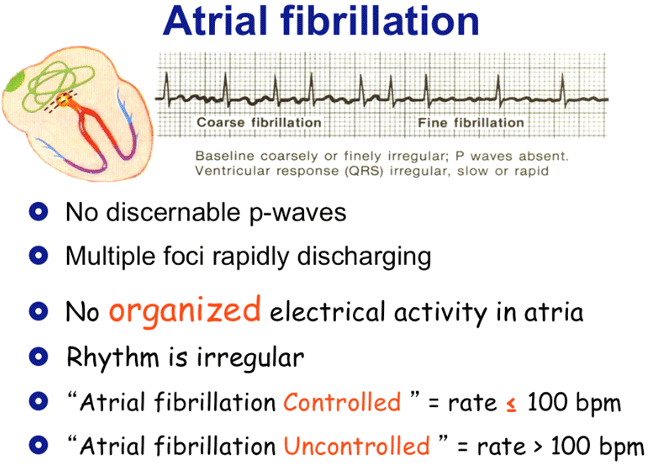
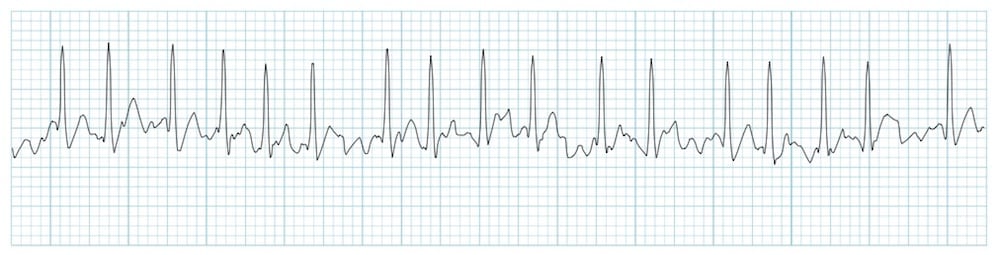
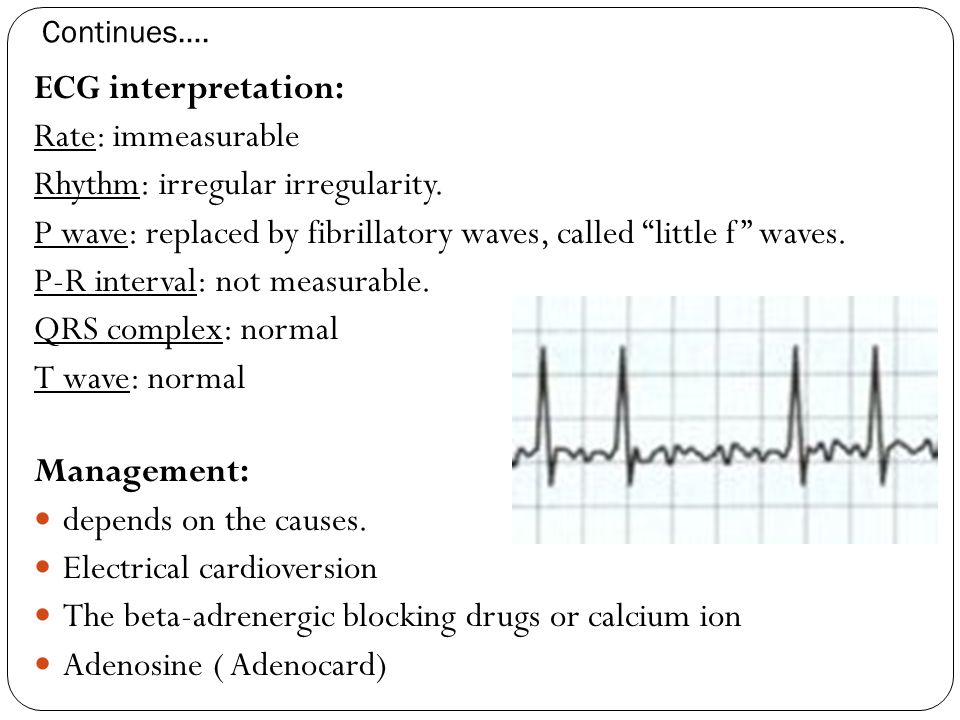
There are fibrillation (f) waves instead of P waves. These signs are indicative of atrial fibrillation or AFib. Although heart rate can be calculated easily by taking a pulse, studies show that an ECG (electrocardiogram) may be necessary to determine if there is any damage to the heart, how well a device or drug is working, whether the heart is beating normally, or to determine the location and size of the heart chambers.
Atrial Fibrillation occurs when multiple electrical impulses occur within within the atria. Not to be confused with f-waves seen in atrial fibrillation) which gives the baseline a saw-tooth appearance. Although elicitable in a variety of muscles, it is best obtained in the small foot and hand muscles.
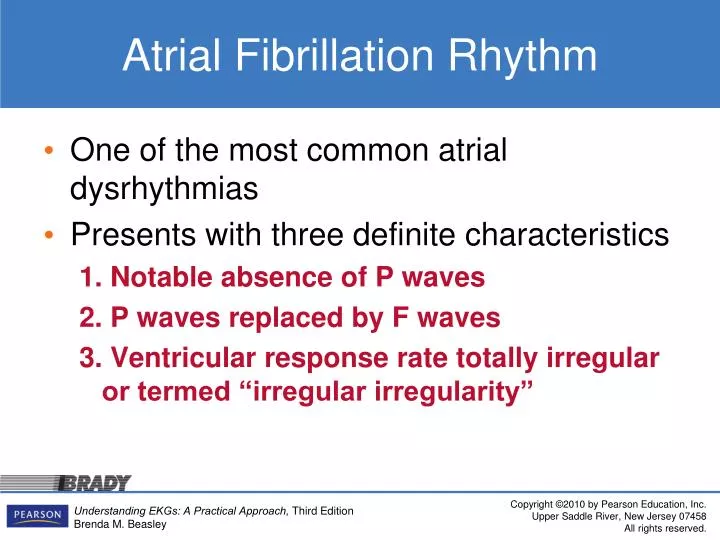
The different waves that comprise the ECG represent the sequence of depolarization and repolarization of the atria and ventricles. The R-R intervals are not equal resulting in an irregular rhythm (irregularly irregular). Electrocardiogram waves, intervals, and segments.
P waves are absent. Surface ECG f Wave Analysis at Initial Onset of Paroxysmal and Persistent Atrial Fibrillation. Small ‘septal’ Q waves are typically seen in the left-sided leads (I, aVL, V5 and V6).
(1)Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University, USA. Electrodes are placed on your chest to record your heart's electrical signals, which cause your heart to beat. Frequently the request is made by practitioners with no particular expertise in cardiology.
When the tip of PICC comes to the ideal position (the lower 1/3 of SVC), f wave amplitude is the highest, which is similar to the change of P wave in the normal surface ECG patients. (supraventricular tachycardia) If the rhythm is like this - It’s “A-Fib” or atrial fibrillation. P waves are absent.
Absent P waves on ECG:. Clear 'flutter waves' can be seen. Send thanks to the doctor.
That doesn’t just mean standing up to high-winds and hail, or whatever else nature throws down. An EKG readout displays R waves to indicate cardiac health. Kashou has taught and developed curriculum for medical students, including 500+ lectures and 100+ hours of adult and pediatric ECG lessons.
Also, as the atrial rate slows with the use of medications, there is a loss of F-wave amplitude and the morphology can become incredibly subtle. The F wave occurs after the direct motor potential or the M response. The absence of a P wave located on an electrocardiogram.
On standard calibration, each large box has sides of 0.5 cm. Therefore, each small 1-mm square represents 0.04. Johnstrude CL, Perry JC, Cecchin F, et al.
This is, in fact, a marked sinus arrhythmia, an ECG finding frequently mistaken for atrial fibrillation. Indeed, a repeat ECG (figure 1C) confirms the presence of P waves. The PRI is indeterminate.
A pattern of irregular undulations of the base line in an electrocardiogram that is indicative of atrial fibrillation. Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia When multifocal atrial tachycardia occurs, multiple (non-SA) sites are firing impulses. Some common causes of R wave abnormalities on an ECG include a thin chest wall or obesity.
Nakayama M, Nakamura J, Hamada Y, Chaya S, Mizubayashi R, Yasuda Y, Kamiya H, Koh N, Hotta N Diabetes Care 01 Jun;24(6):1093-8. A larger upwards deflection, a peak (R);. These electrodes detect the small electrical changes that are a consequence of cardiac muscle depolarization followed by repolarization during each cardiac cycle (heartbeat).
At F Wave, we have one simple mission:. They are the product of the action potentials created during the cardiac stimulation, and repeated from one heart beat to another, barring alterations. EKG tracings will show tightly spaced waves or saw-tooth waveforms (F-waves).
This patient also has evidence of an acute inferior MI as shown by the ST segment elevation in leads III and aVF. Flat t waves are a nonspecific finding, in and of themselves they are of minimal significance. R-wave ≥ 0.04 s in V1–V2 and R/S ≥ 1 with a concordant positive T-wave in the absence of a conduction defect.
P wave is the first short upward movement of the ECG tracing. F response An undulation of an EMG that corresponds to the time between application of a stimulus to the axon of the α motor neuron as it propagates andromically to the anterior horn of the spinal cord, and. So we can associate the P wave of an ECG with the contraction of the atria.
The patient was agitated at the time of the original ECG resulting in an arte factual disturbance of the isoelectric line making the P waves difficult to discern. The atria quiver rapidly, with most electrical impulses being blocked before reaching the ventricles. Inverted U wave, a specific electrocardiographic sign of cardiac ischemia.
The first little “hump” or “bump” you see is known as the P-wave. It indicates that the atria are contracting, pumping blood into the ventricles. This test detects the electrical activity of the heartbeat through electrodes.
Differentiating anomalous left main coronary artery originating from the pulmonary artery in infants from myocarditis and dilated cardiomyopathy by electrocardiogram. » Review Causes of Absent P waves on ECG:. F-waves are the second of two late voltage changes observed after stimulation is applied to the skin surface above the distal region of a nerve, in addition to the H-reflex which is a muscle reaction in response to electrical stimulation of innervating sensory fibers.
Electrocardiography is the process of producing an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG).It is a graph of voltage versus time of the electrical activity of the heart using electrodes placed on the skin. The Q wave represents the normal left-to-right depolarisation of the interventricular septum;. The F-wave is a long latency muscle action potential seen after supramaximal stimulation to a nerve.
The QRS complex, normally beginning with a downward deflection, Q;. Atrial Flutter and Atrial Fibrillation With atrial flutter the 'P' waves are indeterminate. Waves are the different upward or downward deflections represented on the EKG tracing.
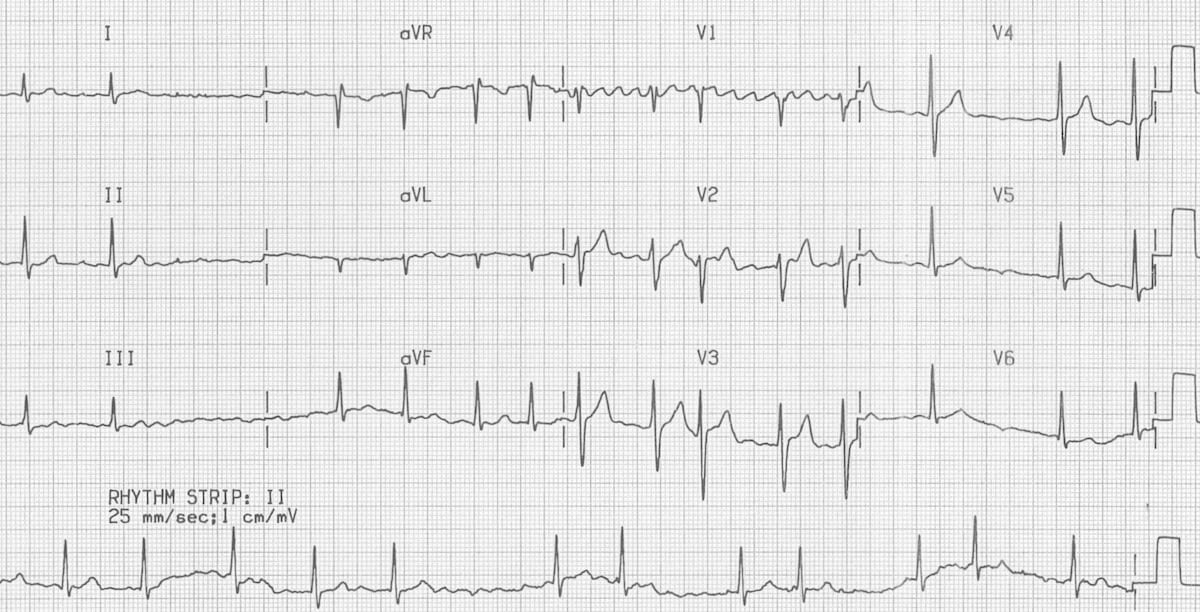
It results from the backfiring of antidromically activated horn cells. Sharma P(1), Barrett TW(2), Ng J(3), Knoten C(3), Ferreira AJ(2), Goldberger JJ(3)(4). The waves of atrial flutter usually best seen in ECG leads 2, 3, and AVF.
They are replaced by lower case "f" waves. If the rhythm is fast - (narrow complex tachycardia without P waves) Then it’s an SVT. ECG in atrial fibrillation The hallmark of atrial fibrillation is absence of P-waves and an irregularly irregular (i.e totally irregular) ventricular rate.
– These are often described as a “saw-toothed pattern.” • There is an absence of discernable P waves when the impulses arise from many different sites in the atria at a rate greater than 350 BPM. Traversal of F-waves along the entire length of periphera. On the horizontal axis, each large box represents 0.2 seconds, and each smaller box.
The baseline (isoelectric line between QRS complexes) is characterized by either fibrillatory waves (f-waves) or just minute oscillations. Cardiology An atrial flutter wave on EKG, which appears as a 'sawtooth' pattern in leads II, III and aVF;. The f waves result in an oscillating irregular baseline.
Anthony Kashou (The EKG Guy) is a. In this setting, the ECG is said to demonstrate a normal sinus rhythm, or NSR. The basic principles of interpretation of the ECG in children are identical to those in adults, but the progressive.
The F wave uses supramaximal stimulation of a motor nerve and records compound muscle action potentials from a muscle supplied by that nerve, along the most proximal segment. If it’s like this - Then it’s a Junctional Rhythm. Inverted T waves may indicate several conditions, including pulmonary embolism, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and heart attack.
The pathological Q waves seen in V1 - V6 indicate that this patient has had an anterior MI in the past. This leads to an extremely high and unproductive atrial rate, but throttled ventricular rate. Massage of the carotid sinus may unmask the flutter waves.
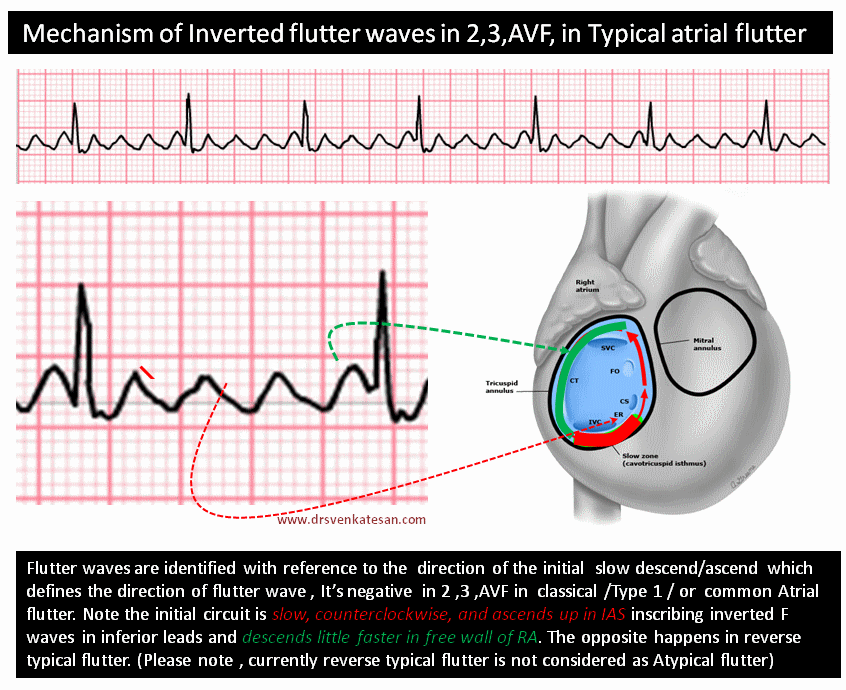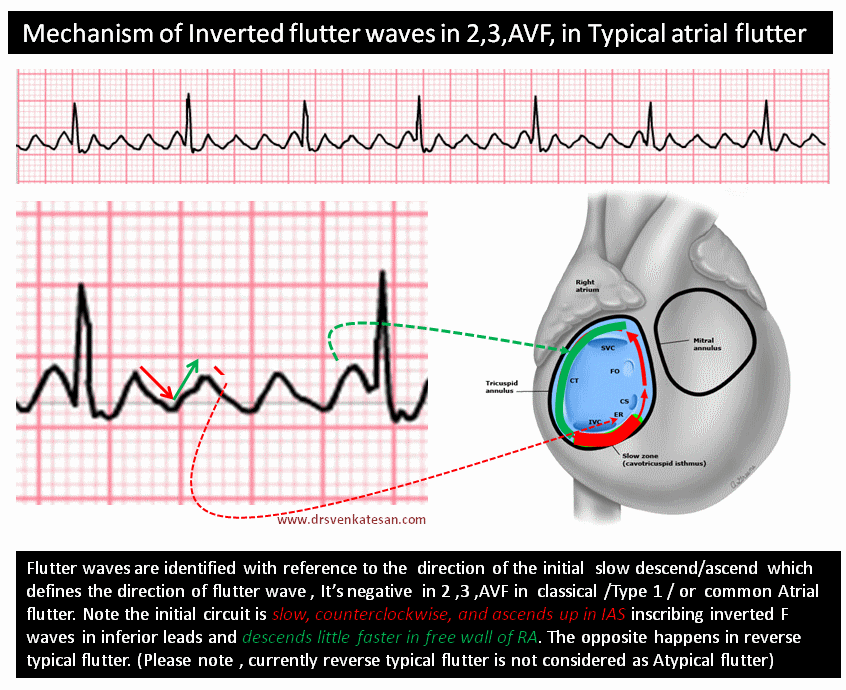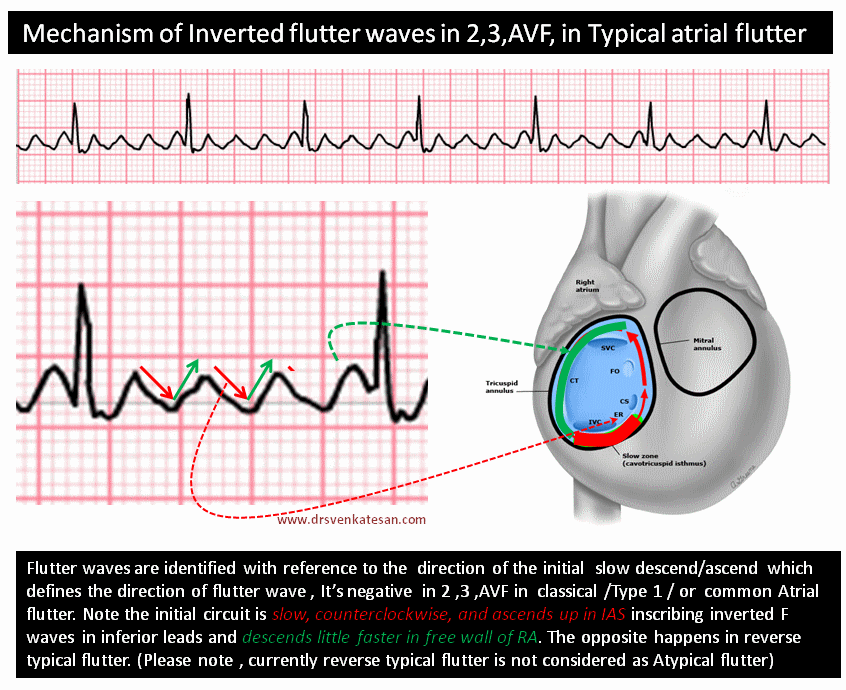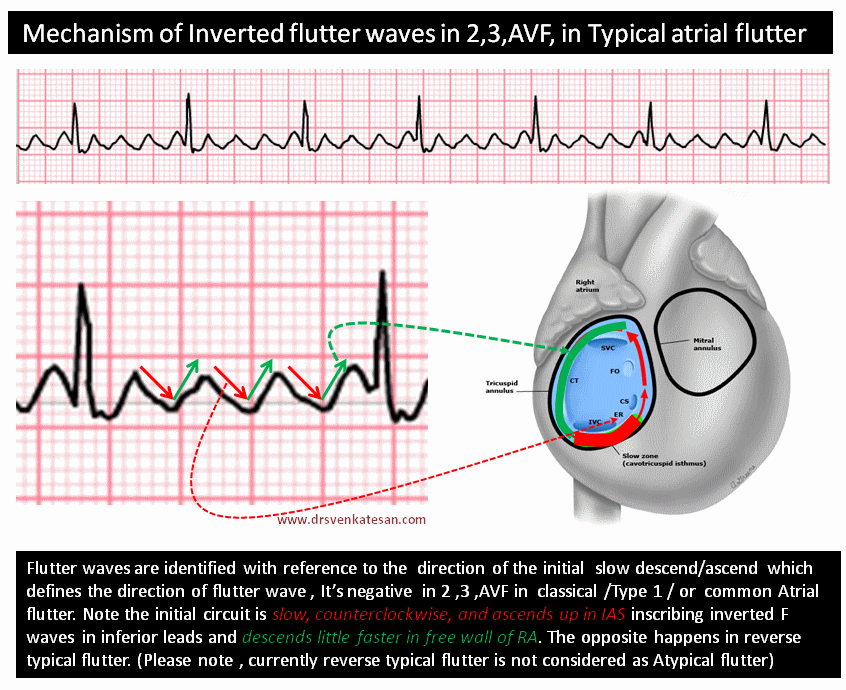
Though this saw tooth pattern is easily recognised , it’s often difficult to say whether the saw is facing upwards or downwards ?. We know, classical Atrial flutter (Also referred to as typical /Common AF) records saw toothed F waves due to continuous atrial electrical activity across a macro- reentrant circuit within right atrium. Remember from the electrical conduction lecture, that the SA node is responsible for this.
The next area you see is a big spike. Absent P waves on ECG:. These need to be present in at least 2 contiguous.
Atrial flutter generates a defined pattern of atrial activity in the EKG with a "sawtooth" pattern in leads II, III, AVF without a defined isoelectric line between F waves (see figure 5a). Sovari AA, Farokhi F, Kocheril AG. The normal U wave has the same polarity as the T wave and is usually less than one-third the amplitude of the T wave.
Cardiologists and other health professionals analyze ECGs to diagnose various cardiac diseases. Causes | Symptom Checker » Causes of Absent P waves on ECG:. No P waves means there is no PR interval measurement.
The P-wave represents ATRIAL DEPOLARIZATION (depolarization is a big, fancy word for CONTRACTION). An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) records the electrical signal from your heart to check for different heart conditions. He is on a mission to transform ECG education and filling the gap exists around the world.
But lead V1 records definite isoelectric lines.

Atrial Fibrillation Topic Review Learntheheart Com

Ecg Amboss
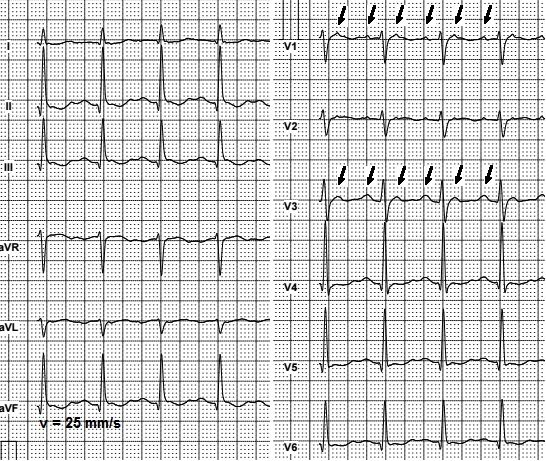
Interpretation Of Uncommon Ecg Findings In Patients With Atrial Flutter
Ppt Atrial Flutter And Atrial Fibrillation Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id

Ecg Amboss
Co Grand Co Us Documentcenter View

Ecg Primer For The Cath What Does A Tall R Wave In V1 Mean The Four Categories Approach Cath Lab Digest
Ppt Atrial Fibrillation Rhythm Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id

Early Differentiation Of Long Standing Persistent Atrial Fibrillation Using The Characteristics Of Fibrillatory Waves In Surface Ecg Multi Leads Scientific Reports
11 Ecg Patterns Of Supraventricular Arrhythmias Thoracic Key

Electrocardiography Cardiovascular Disorders Msd Manual Professional Edition
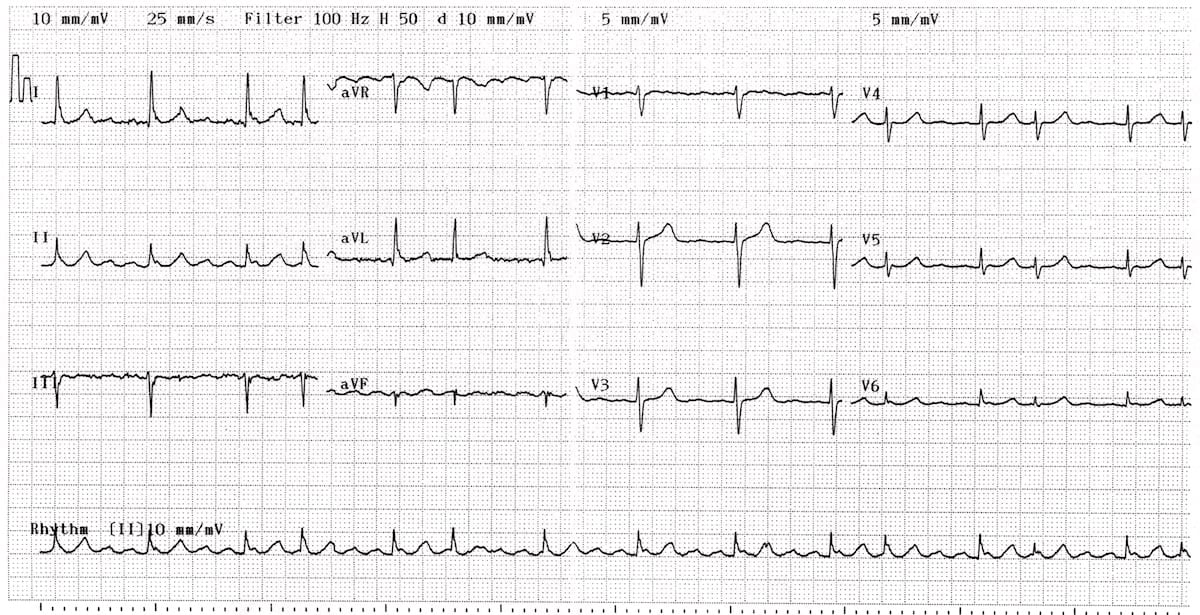
Atrial Flutter Litfl Medical Blog Ecg Library Diagnosis
1
Ecg In Aflutter
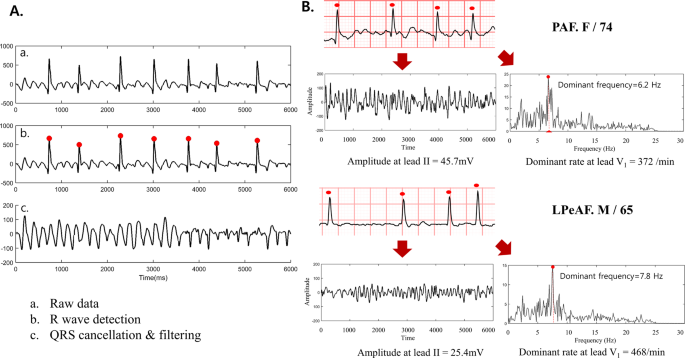
Early Differentiation Of Long Standing Persistent Atrial Fibrillation Using The Characteristics Of Fibrillatory Waves In Surface Ecg Multi Leads Scientific Reports

Ecg Features Of Torsades De Pointes Tdp Torsades Depointes Tdp Diagnosis Cardiology Clinical

The 12 Rhythms Of Christmas Atrial Flutter Ems 12 Lead
Co Grand Co Us Documentcenter View
Atrial Flutter And Atrial Fibrillation

Chapter 3 Supraventricular Rhythms Ii Atrial Fibrillation Ppt Download

Atrial Fibrillation Ecg Classification Causes Risk Factors Management Ecg Echo

Lesson Title Atrial Flutter
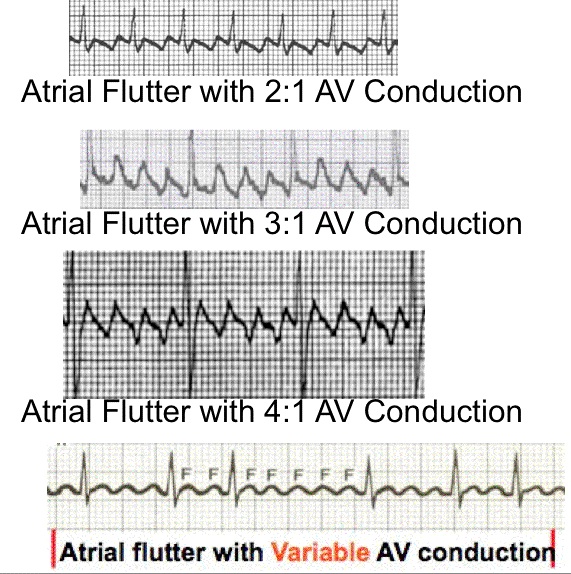
Atrial Flutter And Atrial Fibrillation

The Normal Ecg The Student Physiologist
Lesson Title Atrial Flutter

Ecg In Aflutter

7 Can T Miss Life Threatening Ecg Findings

Ecg A Pictorial Primer Medicine On Line Com

The Extraction Of The F Waves And A Typical Example A Data Download Scientific Diagram

A Representative Example Of An Af Ecg Recording And Its Fiducial Download Scientific Diagram

Ecg Amboss
Lesson Title Atrial Flutter

The 12 Rhythms Of Christmas Atrial Flutter Ems 12 Lead

A Representative Example Of An Af Ecg Recording And Its Fiducial Download Scientific Diagram
Atrial Fibrillation Ecg Classification Causes Risk Factors Management Ecg Echo
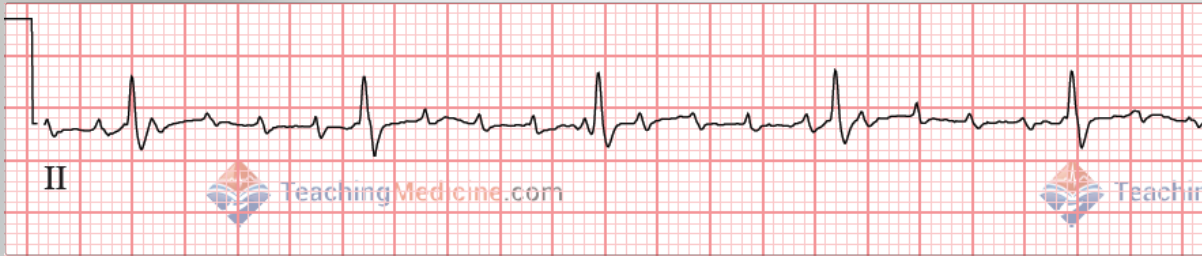
Lesson Title Atrial Flutter
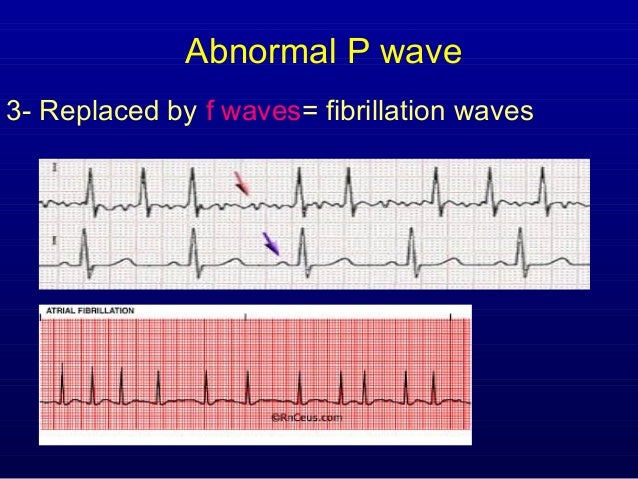
1st Part Ecg Basics Indroduction And P Waves

The 12 Rhythms Of Christmas Atrial Flutter Ems 12 Lead
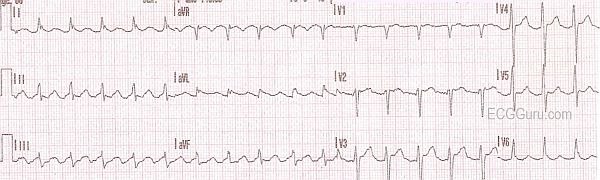
10 Tips To Never Miss Atrial Flutter With 2 1 Conduction
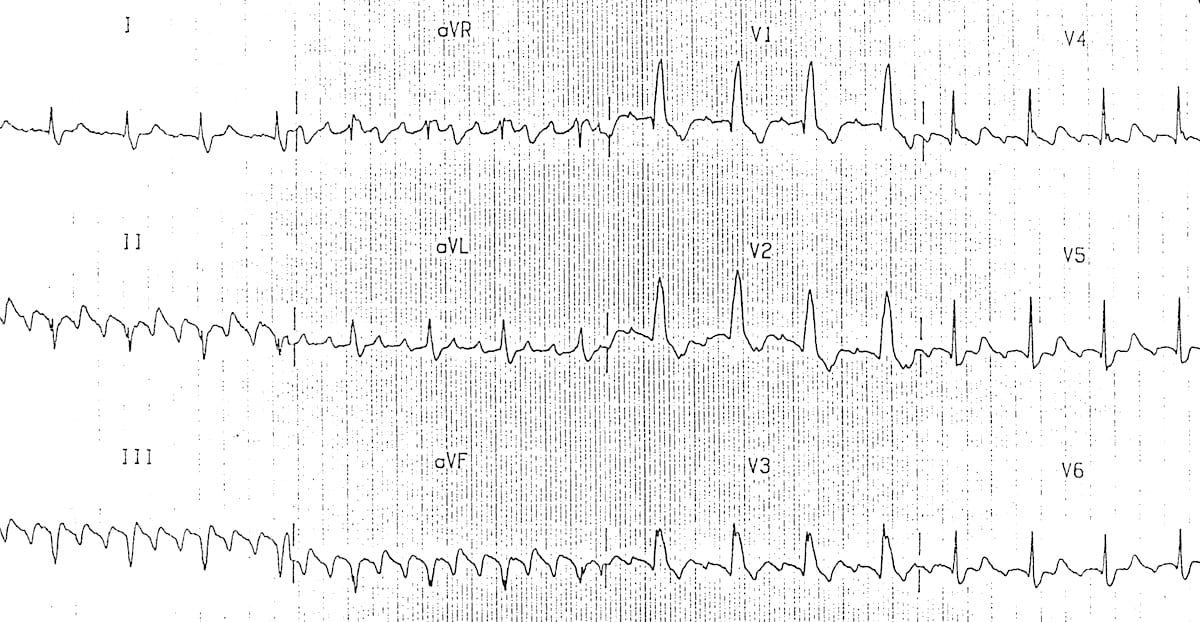
Atrial Flutter Litfl Medical Blog Ecg Library Diagnosis
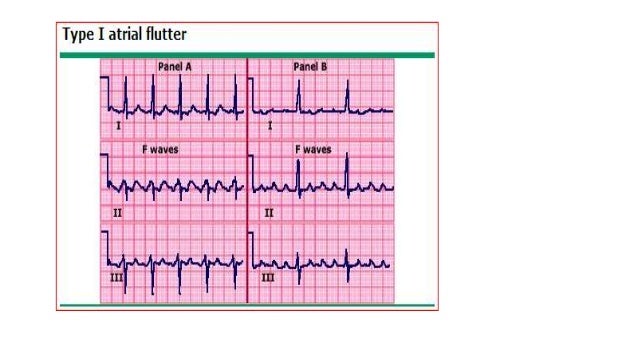
Ecg In Aflutter
Q Tbn 3aand9gcriu0a6yr6 Kpsblb1nf9evv3fhckzri Zbhq Usqp Cau
Atrial Fibrillation Litfl Medical Blog Ecg Library Diagnosis
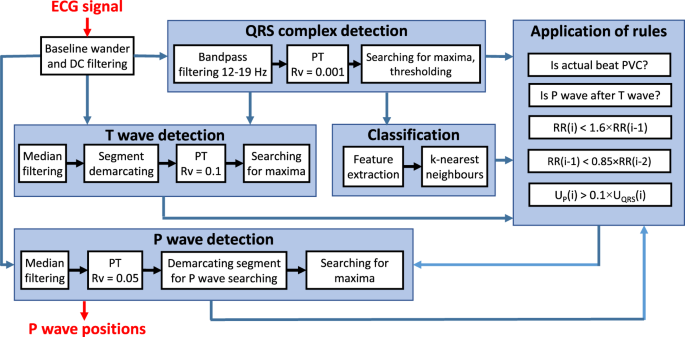
Advanced P Wave Detection In Ecg Signals During Pathology Evaluation In Different Arrhythmia Contexts Scientific Reports
Nursing Management Dysrhythmias Nurse Key
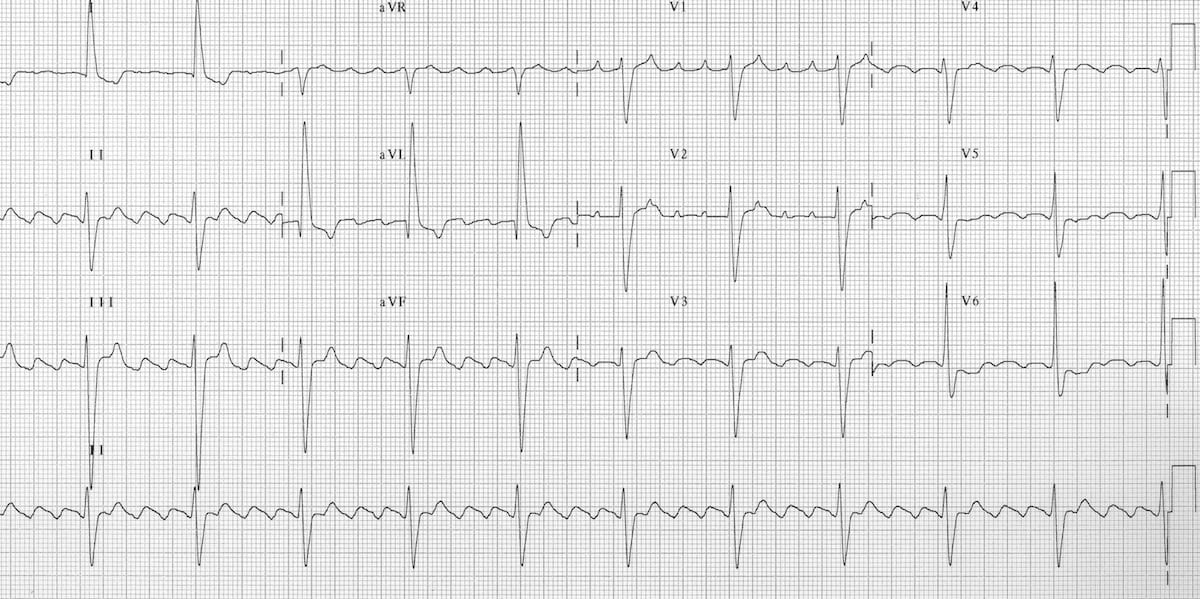
Atrial Flutter Litfl Medical Blog Ecg Library Diagnosis
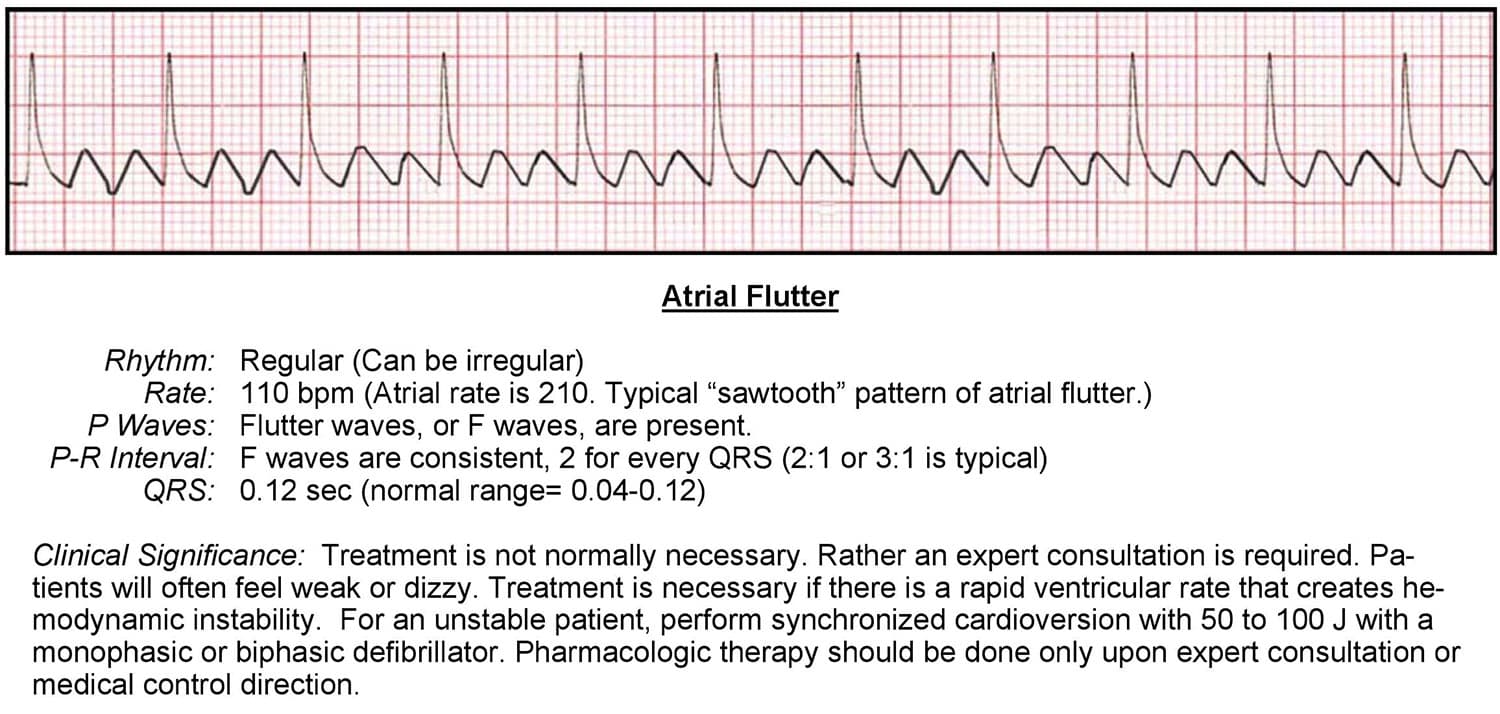
Atrial Flutter Ecg Acls Wiki

Atrial Rhythms Lessons And Quiz

Solved What Is The Heart Rate 60 1 Unable To Determine Chegg Com

Atrial Fibrillation Af Atriyal Fibrilasyon Ekg Ecg Ankara Kardiyoloji Kalp Hastaliklari Mete Alpaslan Doktorekg Com
Atrial Flutter Wikipedia
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq32uyamos1w 5 Fpabv3g 8vqhwbtrgy Pk7dny0aofl4auo8z Usqp Cau

F Waves In Ecg Dr S Venkatesan Md

Normal Ecg Waves Arryhthmias Ppt Video Online Download
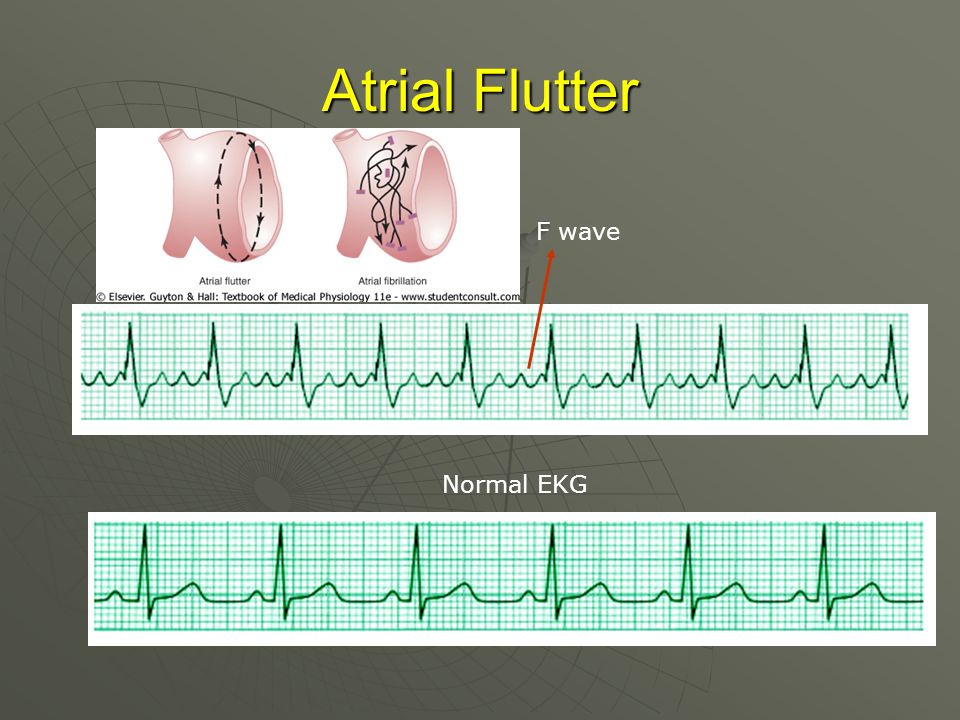
The Physiological Basis Of The Ekg Ppt Download

The 12 Rhythms Of Christmas Atrial Flutter Ems 12 Lead
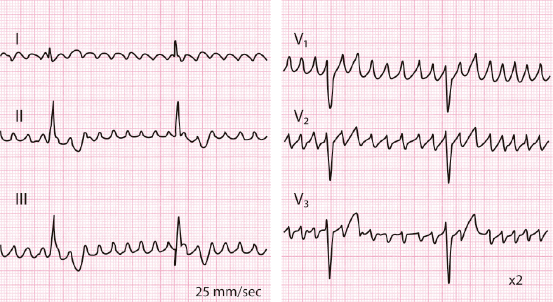
11 Ecg Patterns Of Supraventricular Arrhythmias Thoracic Key
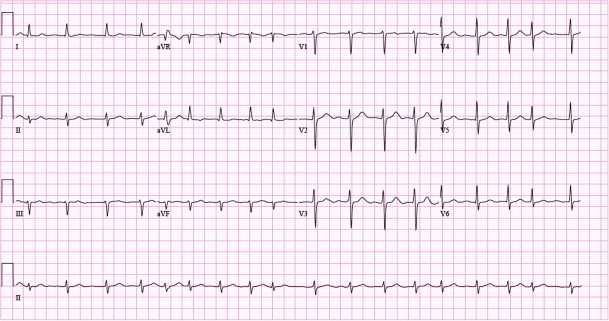
Atrial Fibrillation Ecg Classification Causes Risk Factors Management Ecg Echo

The 12 Rhythms Of Christmas Atrial Flutter Ems 12 Lead

Basic Dysrhythmia Kamlya Balgoon Ppt Video Online Download

Ekg Strips Flashcards Quizlet

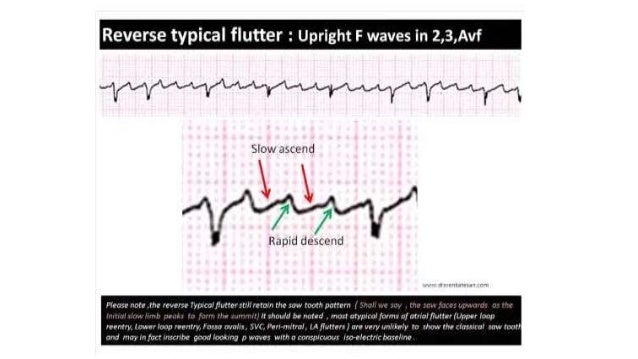
Reverse Typical Clockwise Atrial Flutter On Ekg Inferior Leads Positive Waves

Lesson Title Atrial Flutter

Atrial Fibrillation Ecg Review Criteria And Examples Learntheheart Com

Delineation Of The F Waves For Typical 4 S Segments Corresponding To Download Scientific Diagram

What Is The Difference Between Atrial Fibrillation A Fib Atrial Flutter A Flutter
Q Tbn 3aand9gcqts24zy8 O4ata1y1l95dt16bmfklbcgfih0gkrhxza2ulzs Y Usqp Cau

Understanding The Ekg Signal Atrial Fibrillation Resources For Patients

Atrial Fibrillation Af Atriyal Fibrilasyon Ekg Ecg Ankara Kardiyoloji Kalp Hastaliklari Mete Alpaslan Doktorekg Com
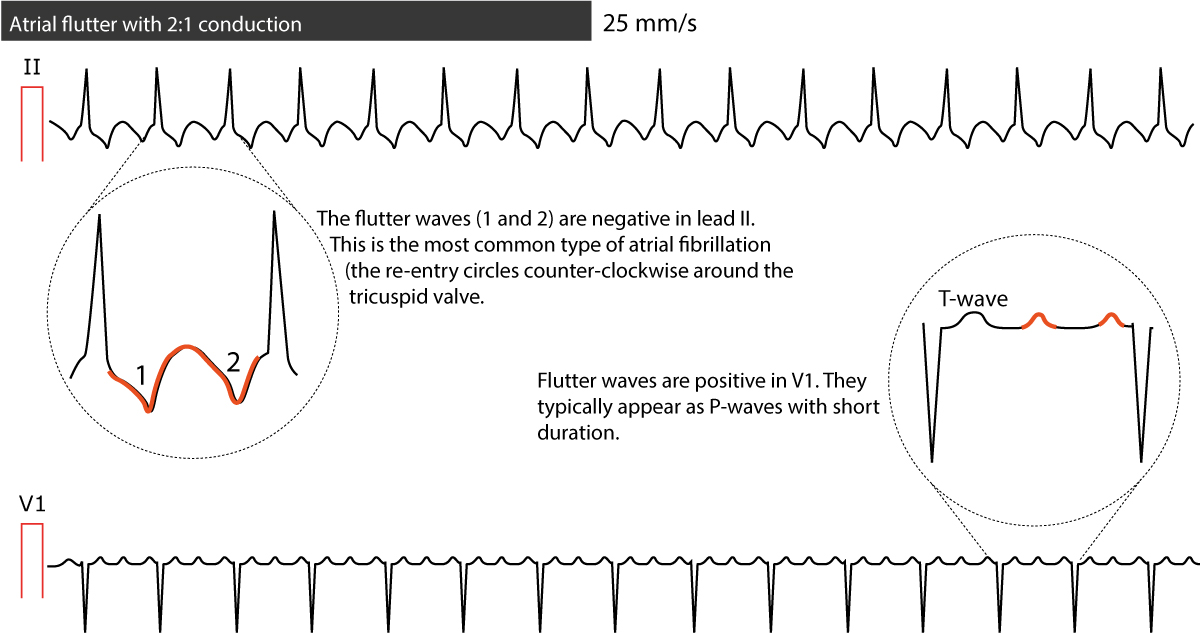
Atrial Flutter Classification Causes Ecg Diagnosis Management Ecg Echo

Conclusion To 68 Yof Cc Unresponsive On Kitchen Floor Osborn Waves Of Hypothermia Ems 12 Lead
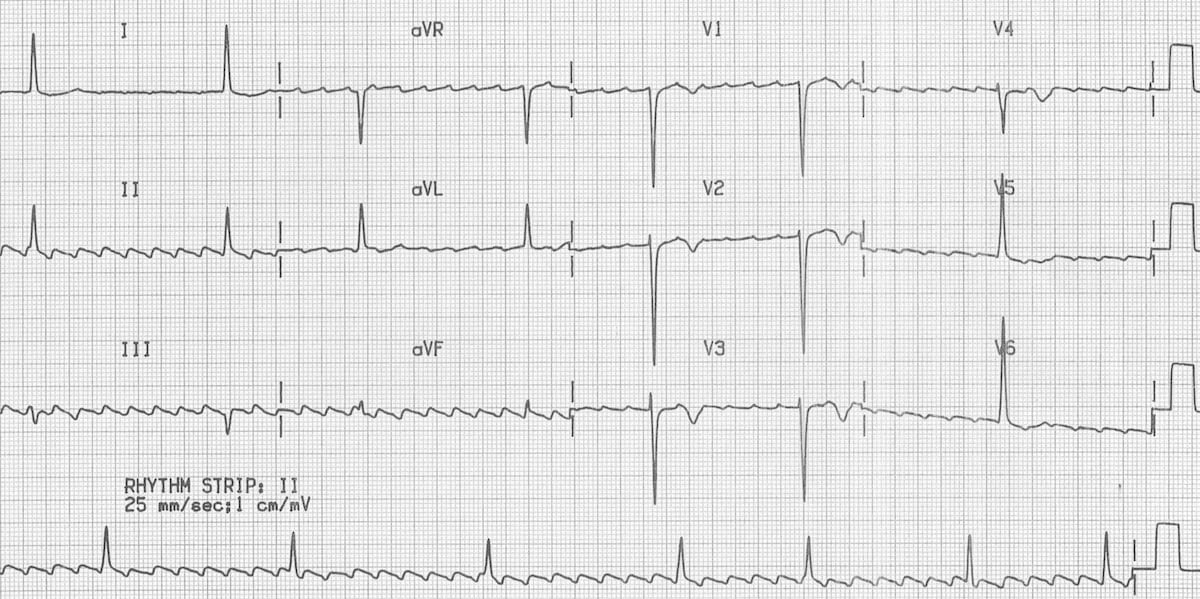
Atrial Flutter Litfl Medical Blog Ecg Library Diagnosis
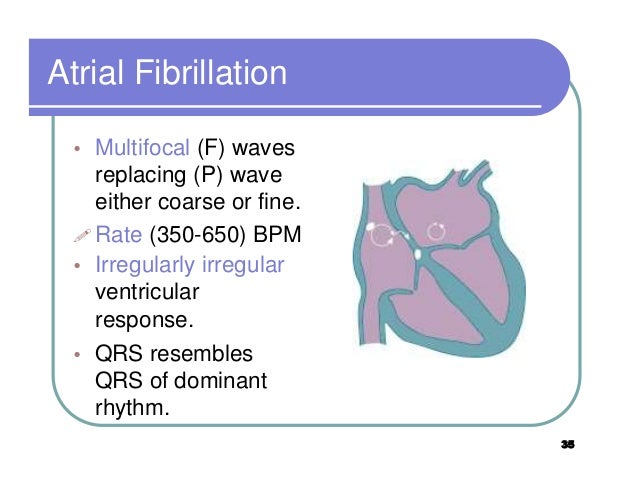
Ecg Step By Step Not By Me

Easy To Understand Different Between Knowledge Of Ecg Facebook

Separating Atrial Flutter From Atrial Fibrillation With Apparent Electrocardiographic Organization Using Dominant And Narrow F Wave Spectra Sciencedirect
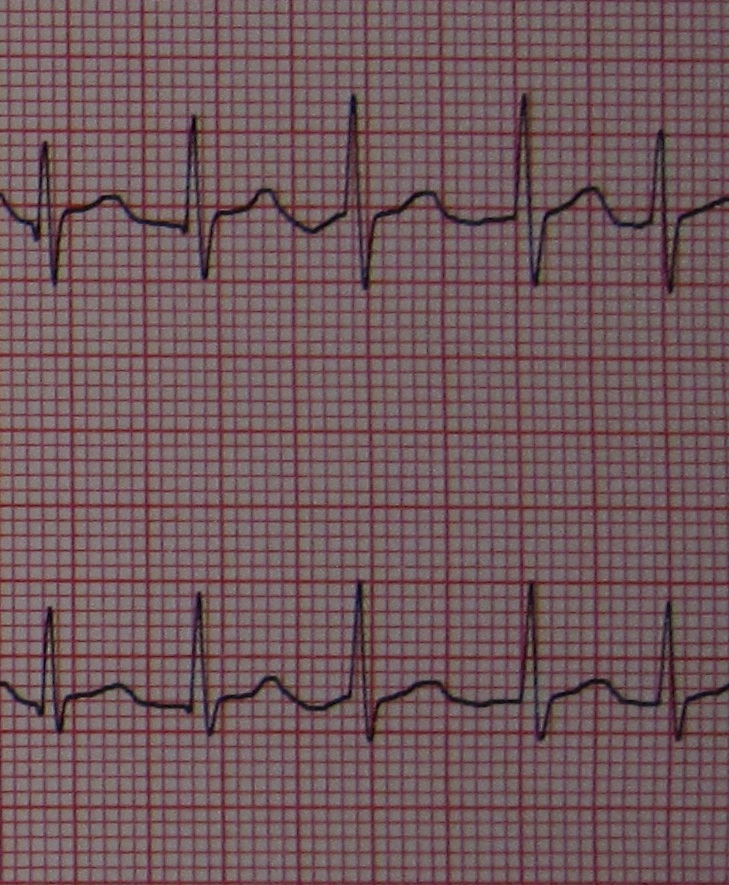
Atrial Fibrillation Wikipedia

Ecg A Pictorial Primer Medicine On Line Com
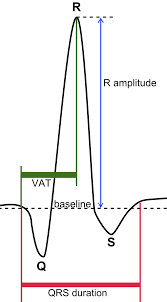
Electrocardiogram Physiopedia

What Is The Difference Between Atrial Fibrillation A Fib Atrial Flutter A Flutter
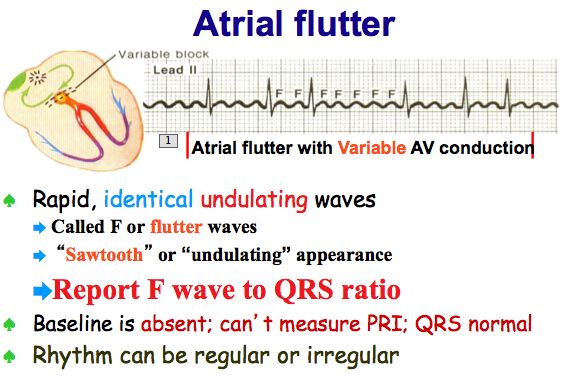
Atrial Flutter And Atrial Fibrillation

Atrial Rhythms Lessons And Quiz

Electrolyte Abnormalities

Pdf Intracardiac Overdrive Pacing As A Treatment Of Atrial Flutter In A Horse
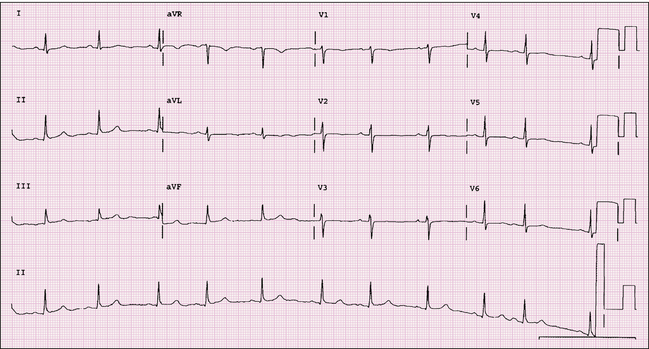
Electrocardiography Radiology Key
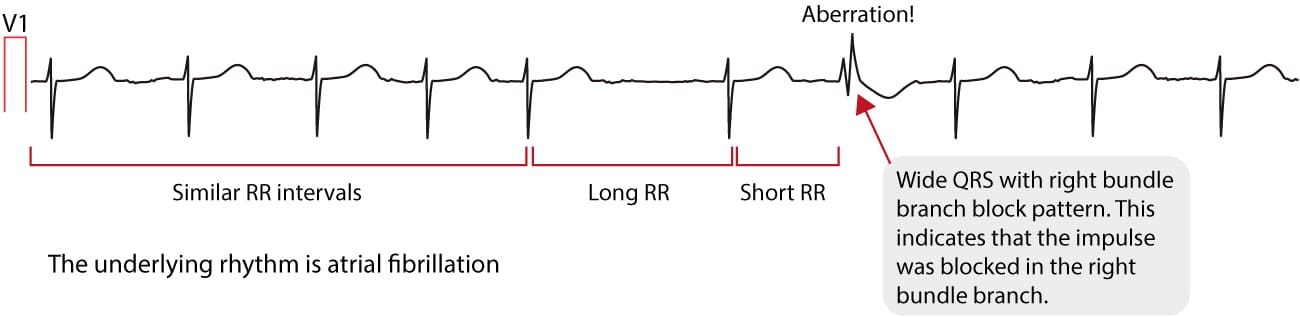
Atrial Fibrillation Ecg Classification Causes Risk Factors Management Ecg Echo

Epsilon Wave An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
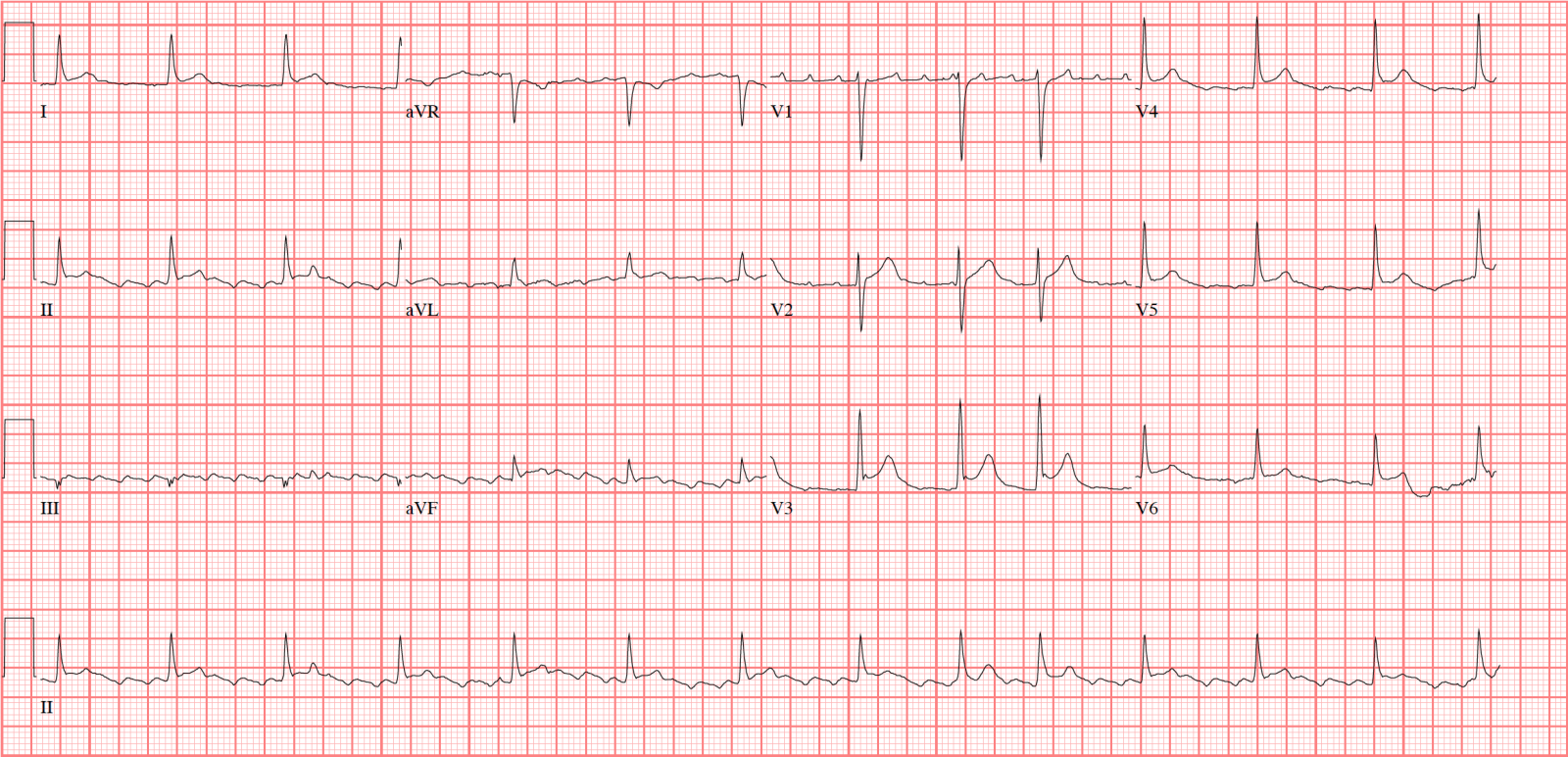
Lesson Title Atrial Flutter

Ekg Strips Flashcards Quizlet
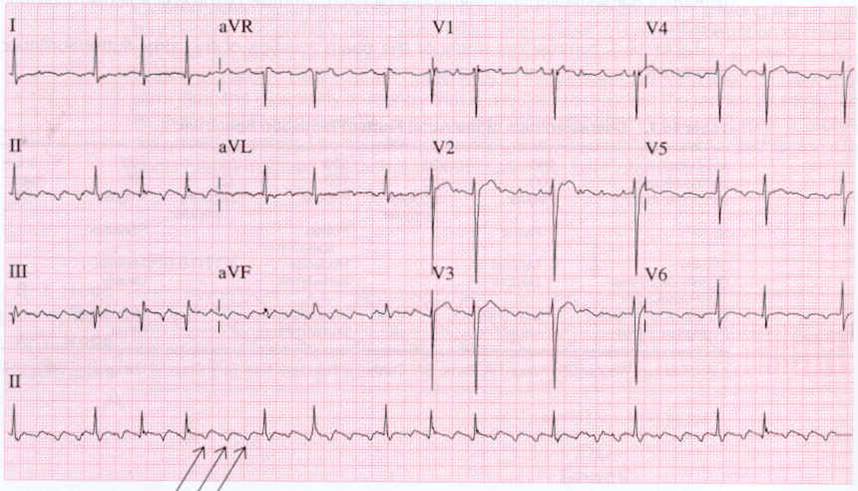
Atrial Flutter Electrocardiogram Wikidoc

Pin On Atrial Flutter
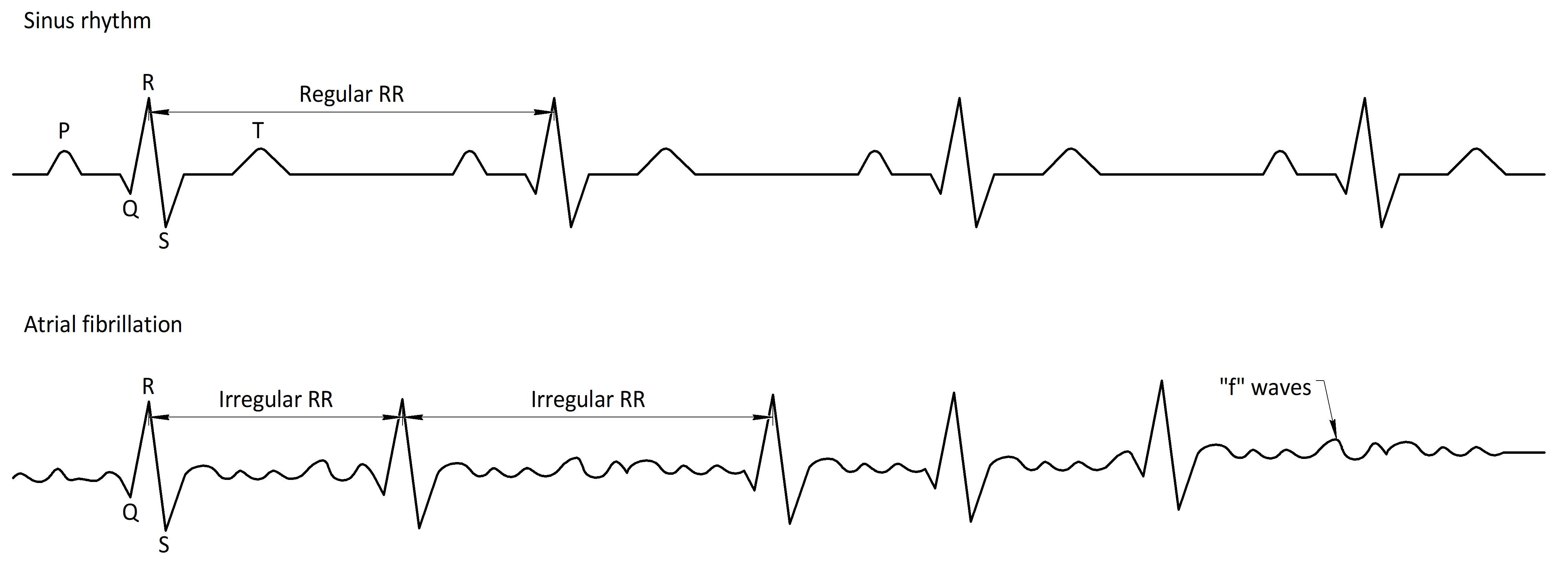
Medicom Afib Detector

Atrial Fibrillation Af Atriyal Fibrilasyon Ekg Ecg Ankara Kardiyoloji Kalp Hastaliklari Mete Alpaslan Doktorekg Com
Atrial Fibrillation Litfl Medical Blog Ecg Library Diagnosis

Atrial Fibrillation Complexity Parameters Derived From Surface Ecgs Predict Procedural Outcome And Long Term Follow Up Of Stepwise Catheter Ablation For Atrial Fibrillation Circulation Arrhythmia And Electrophysiology
Cardiac Arrhythmia Ppt Video Online Download
11 Ecg Patterns Of Supraventricular Arrhythmias Thoracic Key
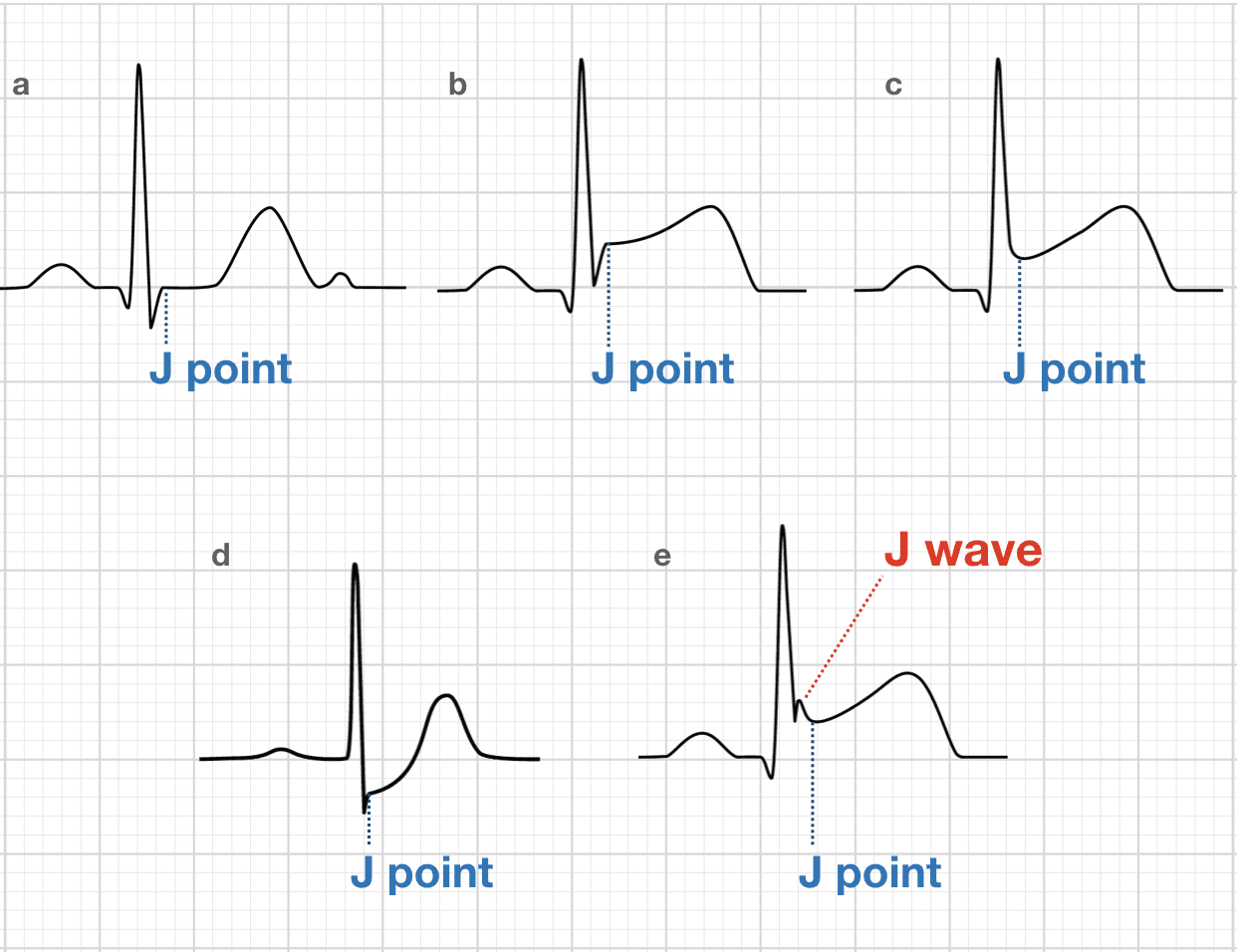
Osborn Wave J Wave Litfl Medical Blog Ecg Library Basics
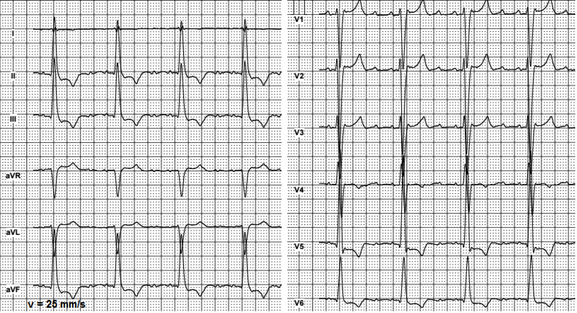
Interpretation Of Uncommon Ecg Findings In Patients With Atrial Flutter



