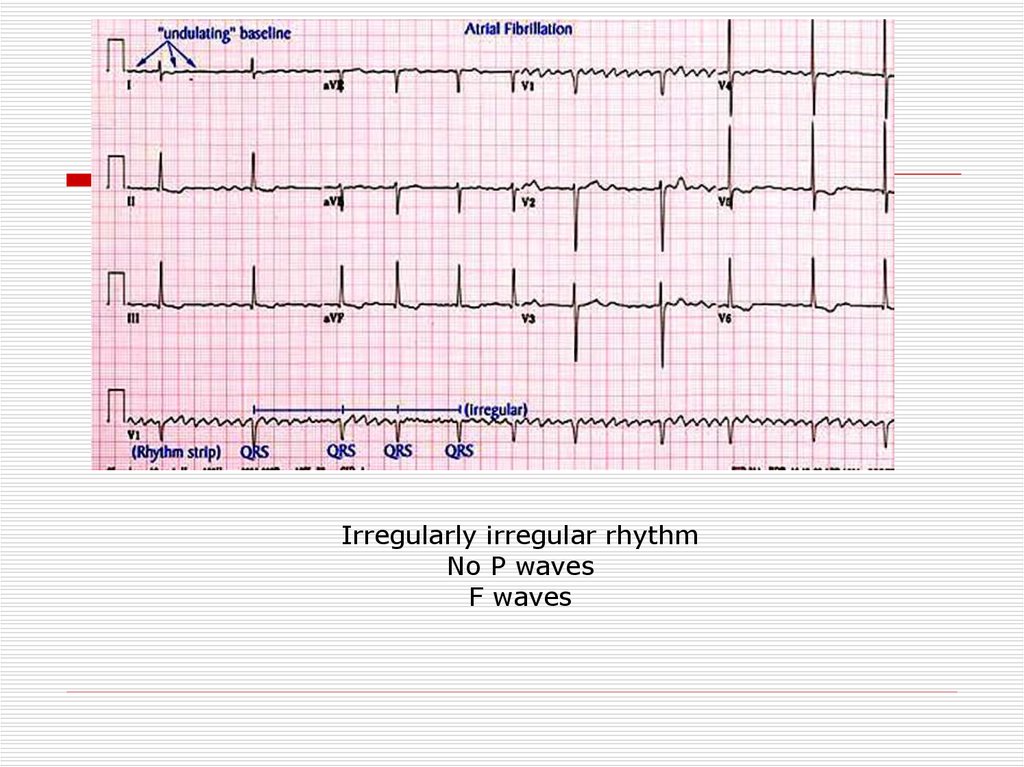
F Waves Atrial Fibrillation
1st Part Ecg Basics Indroduction And P Waves

Atrial Fibrillation Complexity Parameters Derived From Surface Ecgs Predict Procedural Outcome And Long Term Follow Up Of Stepwise Catheter Ablation For Atrial Fibrillation Circulation Arrhythmia And Electrophysiology

Figure 2 From Ladder Diagrams For Atrial Flutter And Atrial Fibrillation Semantic Scholar
Atrial Fibrillation Wikilectures

Pin On Atrial Flutter

Atrial Fibrillation Ekg Reference
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common heart arrhythmia, and 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG) is regarded as the gold standard for AF diagnosis.
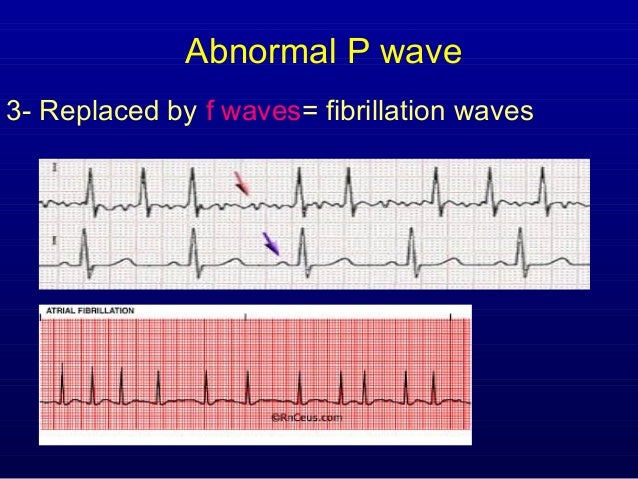
F waves atrial fibrillation. Atrial fibrillation waves (f waves), which are small, irregular waves seen as a rapid-cycle baseline fluctuation, indicate rapid atrial activity (usually between 150. If your symptoms are bothersome or if this is your first episode of atrial fibrillation, your doctor may attempt to reset the rhythm. However, most cardiac conditions may be associated with atrial flutter.
(1)Feinberg School of Medicine, Northwestern University, USA. Atrial fibrillation (AF or AFib) is the most common irregular heart rhythm that starts in the atria. ‘Coarse Afib’ has an “f” wave amplitude> 0.5 mm, which can mimic Aflutter “f” waves morphology.
Screening atrial fibrillation quickly and efficiently remains a challenging task. No P waves means there is no PR interval measurement. Atrial Fibrillation with f Waves.
F response An undulation of an EMG that corresponds to the time between application of a stimulus to the axon of the α motor neuron as it propagates andromically to the anterior horn of the spinal cord, and. It may be difficult to distinguish atypical Aflutter from coarse Afib. Less commonly, F waves are undulating, firing at a rate of 280-3/min, a rate often associated with a 2:1 block and alternating F waves merge with QRS or T waves Neurology.
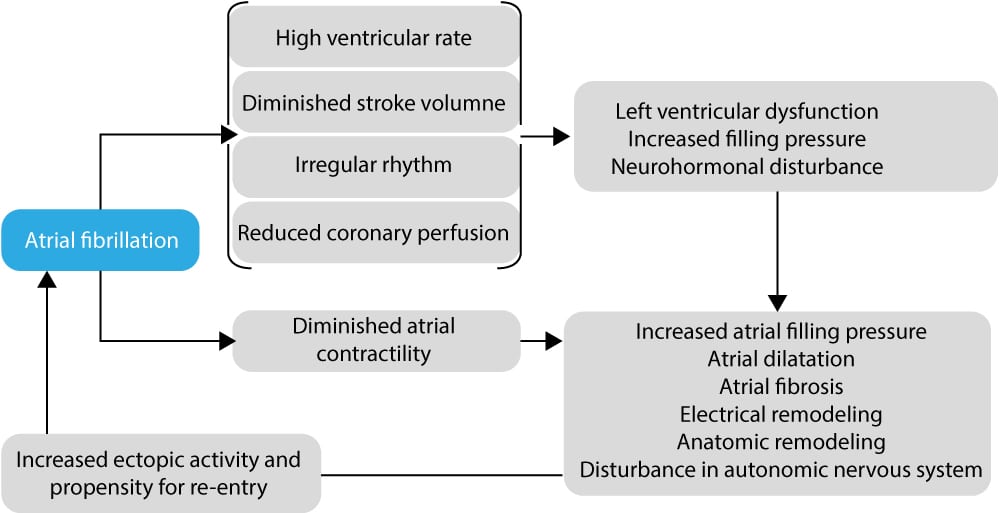
Morbidities include the increased risks of cardiovascular outcomes such as heart failure and stroke and the deleterious effects on quality of life (QOL), functional status, and cognition. Mechanism of Atrial Fibrillation. The amplitude of f-waves may vary from small to large.
Atrial Fibrillation waves (f waves) seen as small irregular waves at rate >150/min Irregularly irregular ventricular rhythm Inconsistent R-R interval, with rates up to rapid rate up to 160-0 bpm in RVR. Muscle tremor or electrical interference may resemble f waves, but the underlying rhythm is regular. (2)Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee, USA.
Most cases of AF are thought to originate in the area of pulmonary vein-left atrial junctions. The waves of atrial flutter usually best seen in ECG leads 2, 3, and AVF. These findings differentiate it from atrial flutter.
Effective and rapid detection of atrial fibrillation is critical to reducing morbidity and mortality in patients. Large f-waves must not be mistaken for flutter waves (F-waves) which are seen in atrial flutter. - re-entrant waves of atrial fibrillation (AF) cannot be localized to any repetitive and stable circuit in the atria.
As only occasional impulses penetrate the atrioventricular node, a totally irregular ventricular rhythm results, which is the. Atrial Fibrillation occurs when multiple electrical impulses occur within within the atria. AFib is the most common type of.
Other irregular rhythms may resemble atrial fibrillation on ECG but can be distinguished by the presence of discrete P or flutter waves, which can sometimes be made more visible with vagal maneuvers. (A lowercase f indicates atrial fibrillation). As in atrial fibrillation, only some of the.
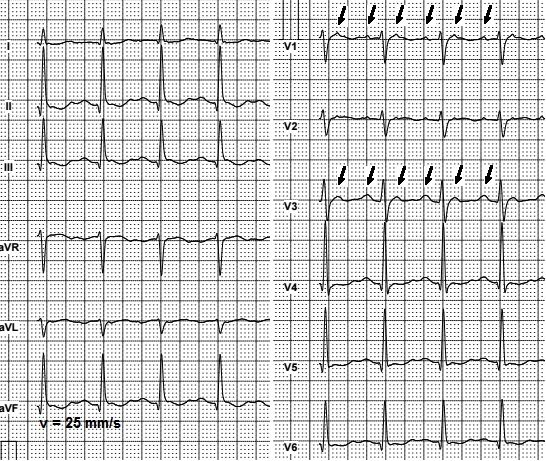
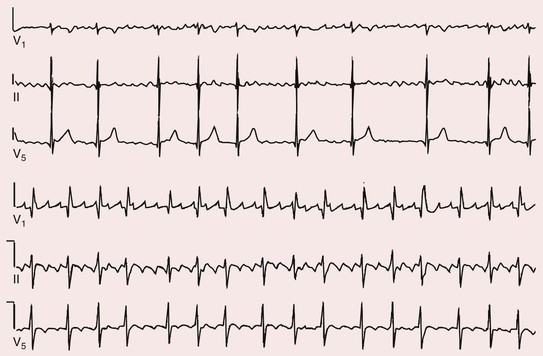
Blood flow from the top chambers of the heart to the bottom chambers varies from beat to beat, and the heart cannot. In this ECG the diagnosis of atrial fibrillation (AF) is not difficult because the fibrillary waves are coarse and easily visible in leads V1 and V2. They both occur when there are problems with the electrical signals that make your heart chambers contract.
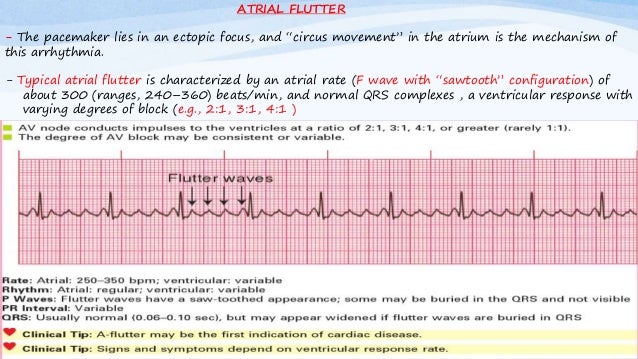
P waves are absent. In AFL, the discharges circulate rapidly at a rate of 300 beats per minute (bpm) around the atrium. This reduces your heart’s ability to pump blood properly and increases the chance of a blood clot forming in your heart and travelling up to your brain, where it can cause a stroke.
No p-waves will be present BUT a wave of f-wave called SAW-TOOTH WAVES. As a noninvasive investigation, F-wave amplitude on TE-ECG may be used as an indicator for the presence of LA-LVAs. F (fibrillation) waves are very clearly seen in this patient with coarse wave atrial fibrillation.
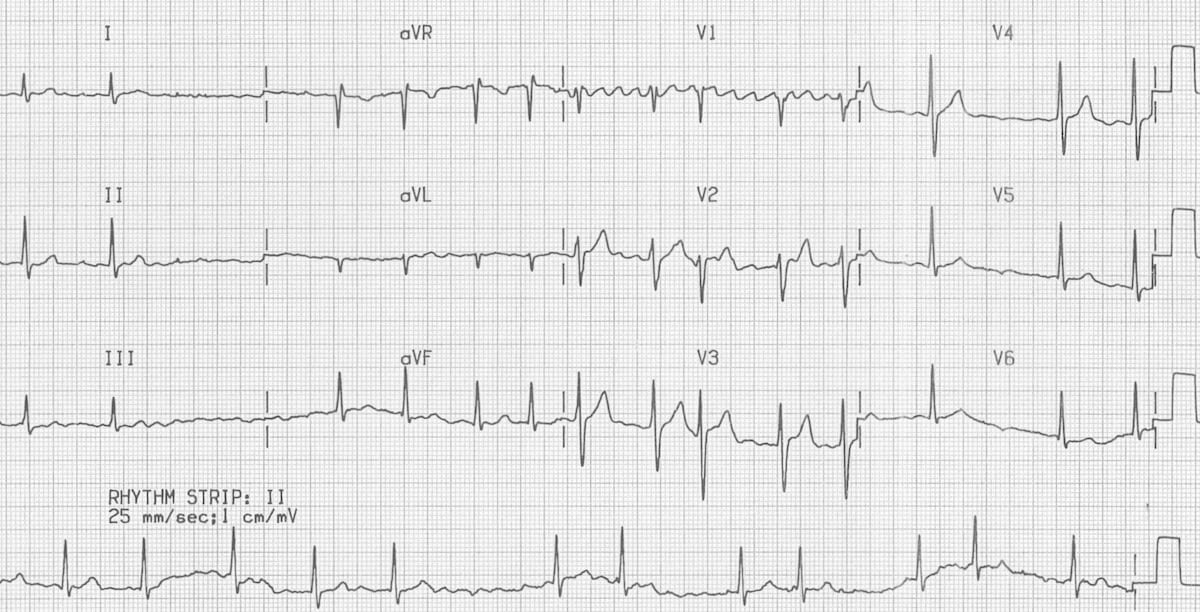
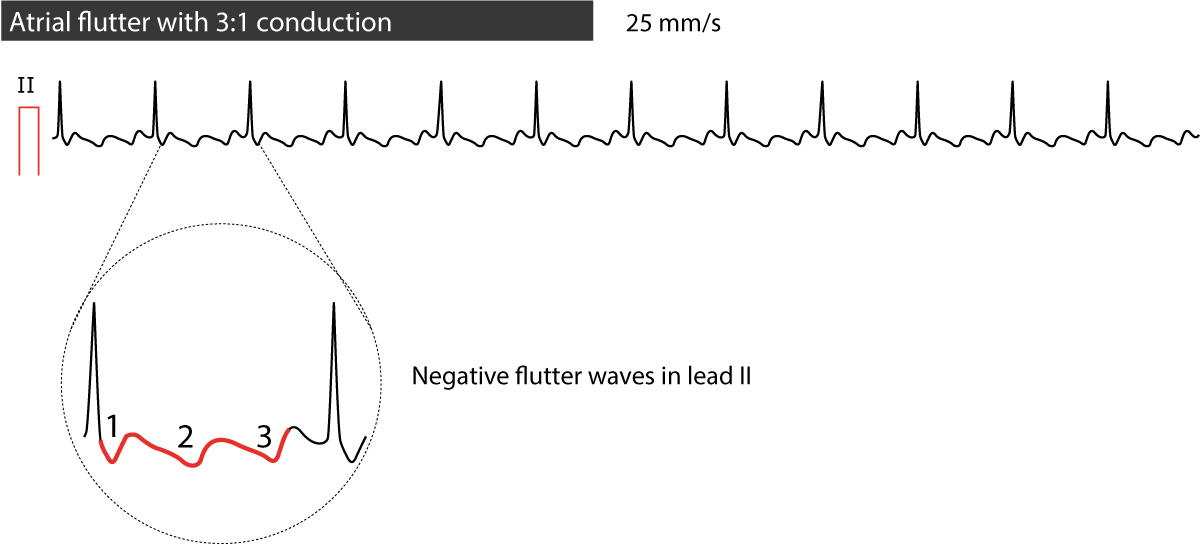
The most common atrial flutter occurs when the atria beat at a rate of 300 bpm and ventricular contraction rate is 150 bpm (2:1 conduction). Atrial fibrillation also referred to as a fib, AFib, A fib, AFIB, AFib and A-fib) is a form of heart disease that causes an irregular and usually rapid heart rhythm that results from abnormal electrical impulses in the upper chambers of the heart (atria) to the AV node. Clear 'flutter waves' can be seen.
They often look like a 'saw tooth' as well. This is a big difference in how you tell if the rhythm is a-flutter or a-fib. If it is effective in eliminating recurrent attacks of atrial fibrillation, then it also eliminates the symptoms caused by atrial fibrillation as well as the risk of blood clots and the risks of.
Atrial fibrillation represents disorganized atrial activity without contraction or ejection. Infrequently, some patients with flutter waves may also have bradycardia because the heart's ventricles are not receiving most of the flutter P waves. AFL produces characteristic saw-toothed F-waves of constant amplitude and frequency on an ECG, whereas AF does not.
Therefore, instead of true P waves, one sees continuous F (flutter) or f (fibrillatory) waves. Recent research shows however that ECG-derived parameters can also be used to assess the spatiotemporal properties of AF. Sometimes you may have atrial flutter that develops into atrial fibrillation and vice versa.
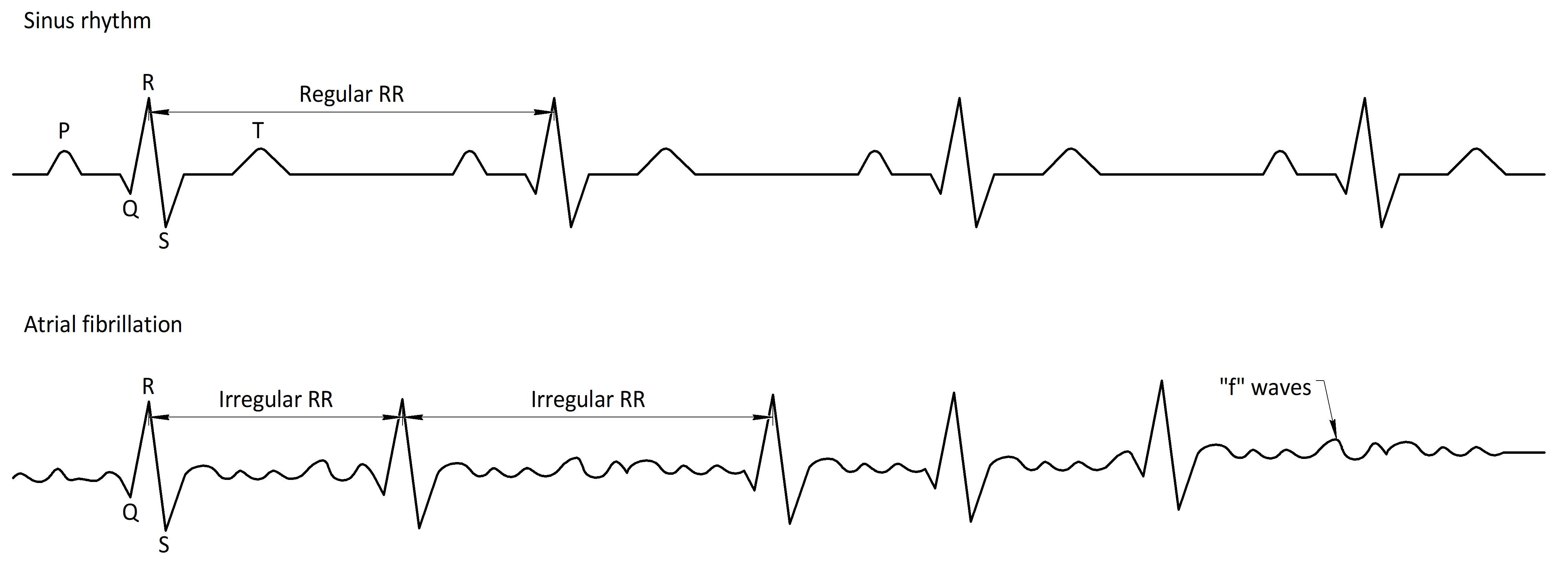
Afib isn't only recognized by the bumps in between QRS complexes, but also by irregular R-R intervals. 6,7 We used a model of increased intra. This chaotic electrical activity results in a chaotic wave form between the QRS complexes.
Not all fibrillatory waves are created equal. This encounter shows an irregular rhythm with no P waves present. In atrial flutter, you will always have the following:.
They are replaced by lower case "f" waves. The atrial rate in atrial flutter is regular, but fast, ranging from 150-400 beats per minute. Though it’s not necessarily harmful by itself, having AFib increases your risk for.
The use of the ECG for atrial fibrillation (AF) in clinical daily practice is still limited to its diagnosis. Atrial fibrillation is the most common arrhythmia encountered in clinical practice. When a patient.
Click here for a more detailed ECG. With time, more and more of the atrial tissue becomes involved in the active maintenance of the arrhythmia, associated with the. Rhythm analysis indicates atrial fibrillation with clear 'flutter waves'.
Atrial fibrillation, also known as AFib or AF, is an electrical disorder of the upper chambers of the heart. We studied 18 atrial fibrillation patients requiring simultaneously a central venous catheter and a trans-esophageal echocardiography. Treating the condition causing atrial fibrillation may help relieve your heart rhythm problems.
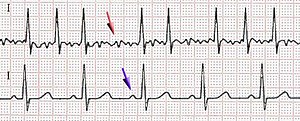
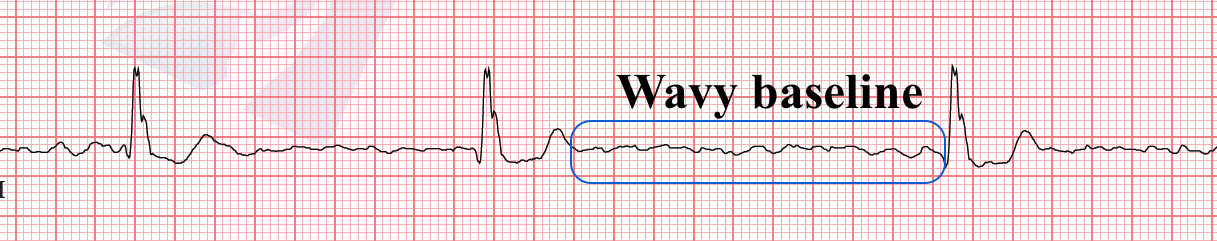
The electrocardiogram demonstrates an irregular baseline where the normal P waves are replaced with rapidly quivering small deflection of variable amplitude (f waves - outlined below). Atrial fibrillation is the most common chronic arrhythmia, characterized by erratic atrial electrical activity with atrial rates of 400 to 600 beats per minute. Fibrillation waves are irregular and are not uniform in shape.
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common arrhythmia of clinical significance (Kirchhof et al., 16).AF is known to increase cardiovascular and all‐cause mortality as well as risk of complications such as ischemic stroke, heart failure, and dementia (Kirchhof et al., 16).Identifying patients at risk of developing AF is important in preventing AF‐related complications. Atrial fibrillation (AF) is of public health importance and profoundly increases morbidity, mortality, and health-related expenditures. With atrial flutter the 'P' waves are 'flutter' waves.
Because the electrical impulses are so fast and chaotic, the atria cannot. Atrial fibrillation (AF or Afib) is a type of arrhythmia in which your heart beats irregularly and often fast. Specifically, the complexity of the f-waves in the ECG reflects the ….
The little bumps in between QRS complexes do seem like p-waves, but depending on the strength of the atrial fibrillations, there may be no bumps at all. Introduction Electrical cardioversion (ECV) is an established therapy for the management of persistent atrial fibrillation (AF). Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a major risk factor of stroke, is associated with severity of stroke and is a common disease with ageing.1–3 Atrial premature complexes (APCs) are found in healthy subjects.4 However, APCs are also associated with cardiovascular death5 and ischaemic stroke.6 In the general population, the detection of even a single APC by ECG is associated with AF.
Atrial fibrillation is the most common arrhythmia and is associated with high morbidity and mortality from stroke, heart failure, myocardial infarction, and cerebral thrombosis. 4,5 Recently, selective PV angiography in patients with paroxysmal AF suggested that AF triggers are most frequently located in dilated superior PVs. Atrial fibrillation is an abnormal heart rhythm, also known as an arrhythmia.
The cardinal features of atrial fibrillation are an absence of coordinated depolarisation of the atria (absence of P waves on the ECG/EKG) and unpredictable depolarisation of the ventricles (no pattern to R wave occurrence on the. 78 year old female patient monitored during superior mesenteric embolectomy. Atrial flutter occurs almost exclusively among persons with significant heart disease, predominantly ischemic heart disease.
The PRI is indeterminate. The procedure uses radio waves to destroy the tissue in the heart that is triggering the abnormal electrical rhythms that cause atrial fibrillation. Atrial flutter is typically due to a large reentrant wave, originating in the right atrium by a premature atrial complex.
Figure 15-1 Diagram comparing mechanisms of atrial flutter and atrial fibrillation (AF). Because the atrial rate is so fast, and the action potentials produced are of such low amplitude, P waves will not be seen on the ECG in patients with atrial fibrillation. Atrial fibrillation may also cause a phenomenon that mimics ventricular extrasystoles or.
Normally, our heart muscle contractions are initiated from an electrical impulse in the right atrium in the sinoatrial sinus. Cardiology An atrial flutter wave on EKG, which appears as a 'sawtooth' pattern in leads II, III and aVF;. The pulmonary veins (PVs) are known to play a critical role in AF.
Generally, f waves are not this large in patients with AF. Misdiagnosis of atrial fibrillation carries significant implications for patients. Atrial flutter and atrial fibrillation (AFib) are two types of abnormal heart rhythm.
The "f" waves can be coarse (majority measure 3 mm or more) or. Focal activation – In which AF originates from an area of focal activity. Click here for the Atrial Flutter YOUTUBE lecture video Click here for the Atrial Fibrillation YOUTUBE lecture video.
Atrial flutter is the second most common pathological tachyarrhythmia. The mechanisms underlying AF are not fully understood but it requires an initiating event (focal atrial activity / PACs) and substrate for maintenance (i.e. Surface ECG f Wave Analysis at Initial Onset of Paroxysmal and Persistent Atrial Fibrillation.
Coarse AF indicates atrial enlargement. This will NEVER be present in a-fib. Although ECV is initially successful, recurrence rates of 70–80% have been reported at follow-up at 1 year.1 Fibrillatory waves (Fw) can often been seen on the surface ECG in AF and can be characterised simply and reliably based on their amplitude.2 Amplitudes of.
Atrial Fibrillation occurs when multiple electrical impulses occur within within the atria. Atrial flutter and atrial fibrillation (AFib) are both types of arrhythmias. Patient has a history of mitral stenosis.
During atrial fibrillation the atrial impulses discharge at a rate of 350-600 per minute, resulting in small (or “fine”), irregular f (fibrillation) waves. Fibrillatory wave amplitude on transesophageal ECG as a marker of left atrial low-voltage areas in patients with persistent atrial fibrillation. Only atrial fibrillation is more common.
Atrial flutter is similar to atrial fibrillation, but the rhythm in your atria is more organized and less chaotic than the abnormal patterns common with atrial fibrillation. Highly accurate diagnosis of AF based on 12-lead ECG is valuable and remains challenging. Atrial fibrillation (AF) often associates with atrial dilatation, 1–3 but the underlying electrophysiological mechanisms remain unclear.
Both conditions can make your heart beat too fast -- but in a different way. Sharma P(1), Barrett TW(2), Ng J(3), Knoten C(3), Ferreira AJ(2), Goldberger JJ(3)(4). Network can learn to use F waves-related features to make classification.
The P wave is absent on the surface. Atypical Aflutter may have varying AV conduction, which can cause an irregular heart rhythm. Report the F wave to QRS ratio.
Resetting your heart's rhythm. Previous reports suggested that intracavitary electrocardiographic method might also be applied to patients with atrial fibrillation, considering the so-called f waves as a surrogate of the P wave. Fibrillatory waves are small with varying morphology and high frequency (300 to 600 waves per minute).
Instead of the SA node (sinus node) directing the electrical rhythm, many different impulses rapidly fire at once, causing a very fast, chaotic rhythm in the atria. P-waves are not present so you can’t measure if the p-waves are regular. The amplitude of these waves varies and may be especially prominent (or “coarse”) in lead V1.
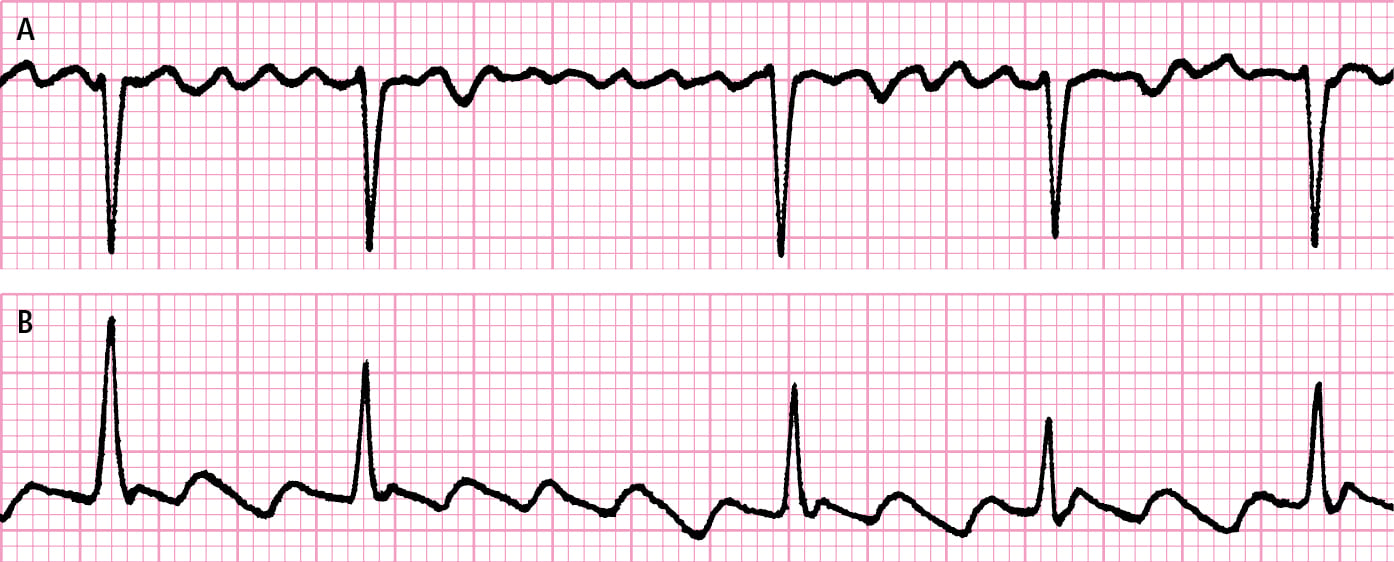
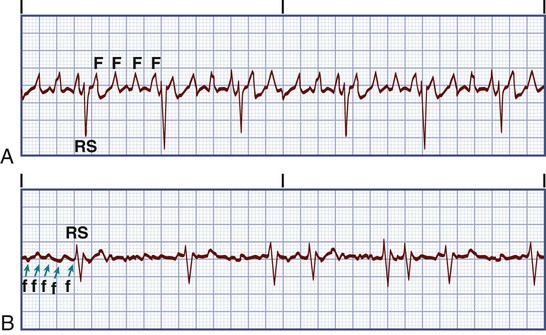
Figure 031 5035 Atrial Fibrillation And Atrial Flutter A Polymorphic F Waves Replacing P Waves During Atrial Fibrillation B Monomorphic Biphasic F Waves Replacing P Waves During Atrial Flutter Mcmaster Textbook Of

Atrial Fibrillation Ecg Classification Causes Risk Factors Management Ecg Echo

Arrhythmia 3 Mph9 Sunderland Studocu
Interpretation Of Uncommon Ecg Findings In Patients With Atrial Flutter
Atrial Fibrillation Ecg Classification Causes Risk Factors Management Ecg Echo

Atrial Flutter And Atrial Fibrillation Chapter Ppt Download

Ekg Final Clp Flashcards Quizlet

Acute Management Of Atrial Fibrillation Part I Rate And Rhythm Control American Family Physician

Atrial Fibrillation Ecg Review Criteria And Examples Learntheheart Com
Q Tbn 3aand9gcqd5hwdwpwg5ur3ji Zbas6f3i7 0qjfamk Gqtspz Fl9sddo Usqp Cau
Cardiac Arrythmia In Children
Lesson Title Atrial Fibrillation
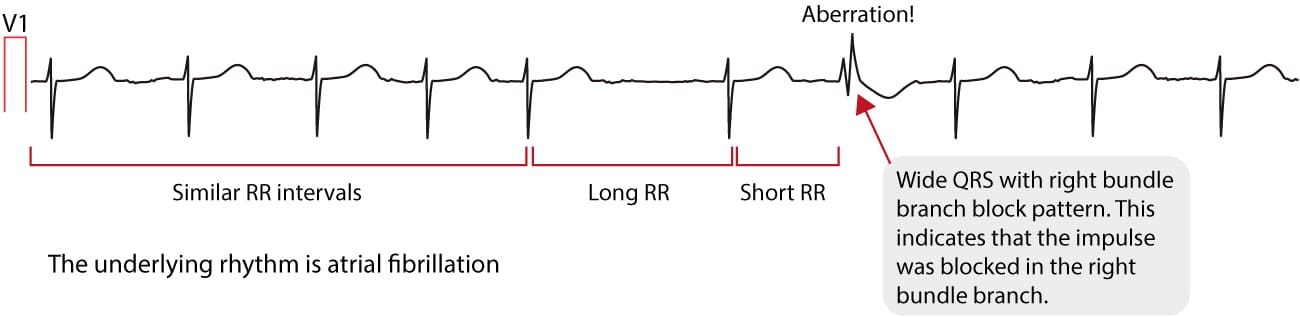
Atrial Fibrillation Ecg Classification Causes Risk Factors Management Ecg Echo

What Is The Difference Between Atrial Fibrillation A Fib Atrial Flutter A Flutter

Atrial Fibrillation Basics Off Label

Pdf F Wave Amplitude Stability On Multiple Electrocardiogram Leads In Atrial Fibrillation Semantic Scholar

Medicom Afib Detector
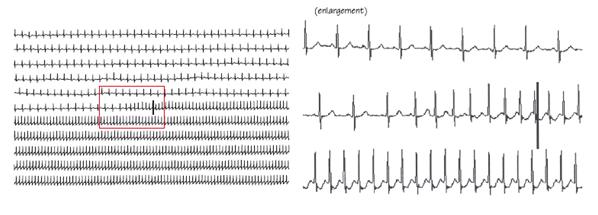
Palpitations Thoracic Key

Atrial Fibrillation Complexity Parameters Derived From Surface Ecgs Predict Procedural Outcome And Long Term Follow Up Of Stepwise Catheter Ablation For Atrial Fibrillation Circulation Arrhythmia And Electrophysiology

Atrial Fibrillation Topic Review Learntheheart Com
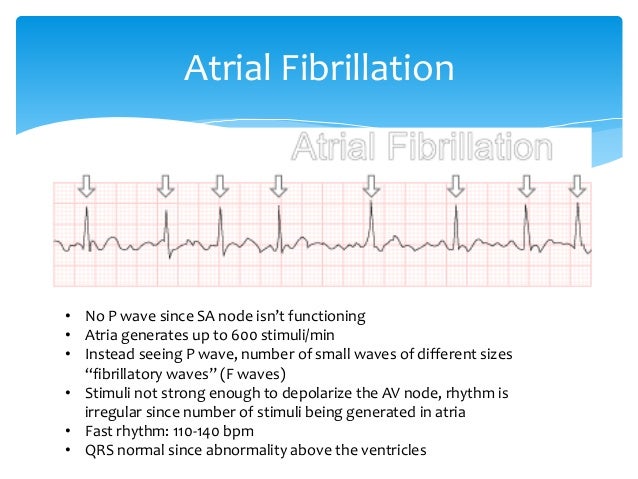
Electrocardiography
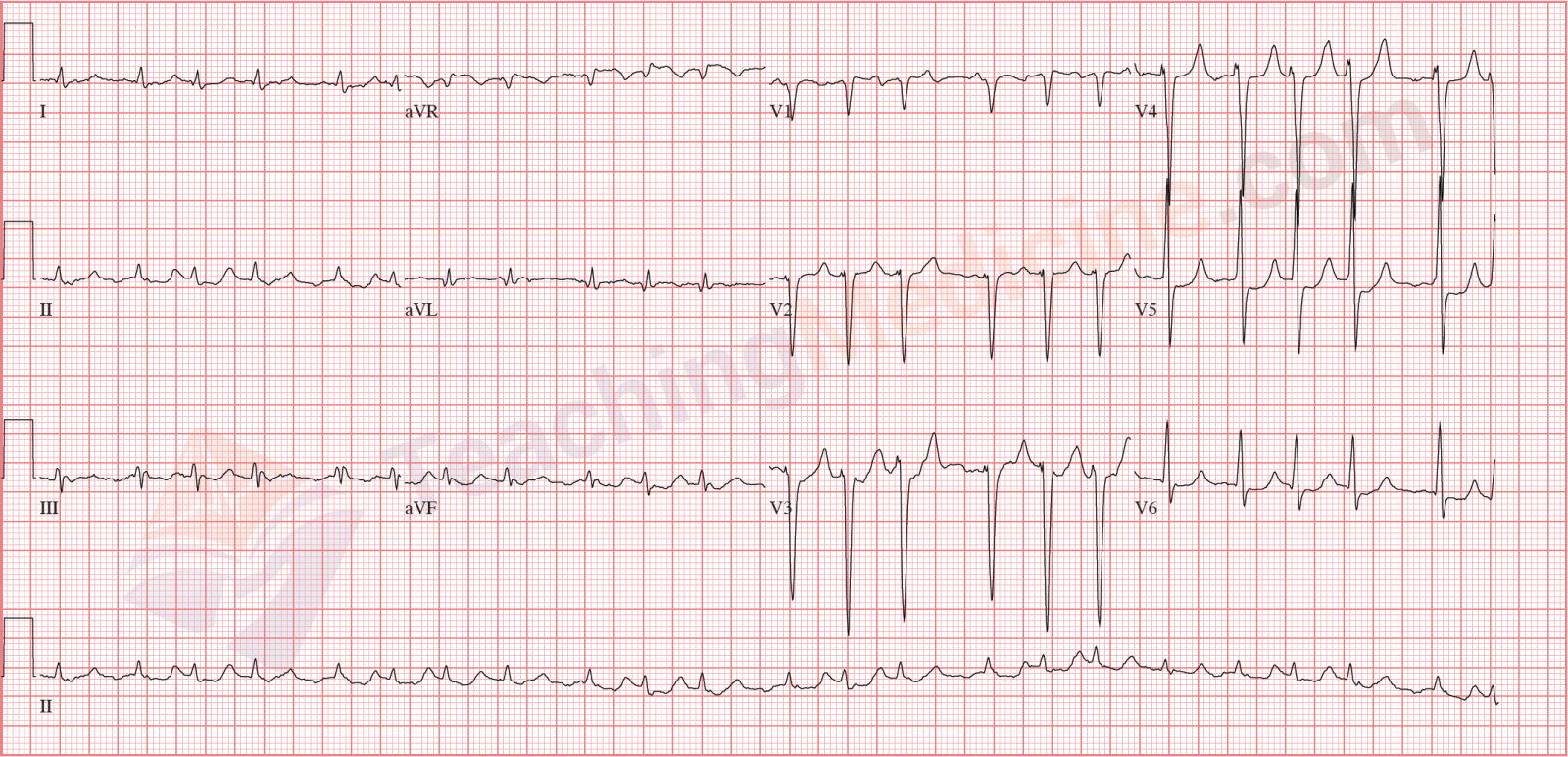
Lesson Title Atrial Fibrillation

This Simple Question In Atrial Flutter Ecg Bothered Me For Long Is The Saw Tooth Upright Or Inverted Dr S Venkatesan Md
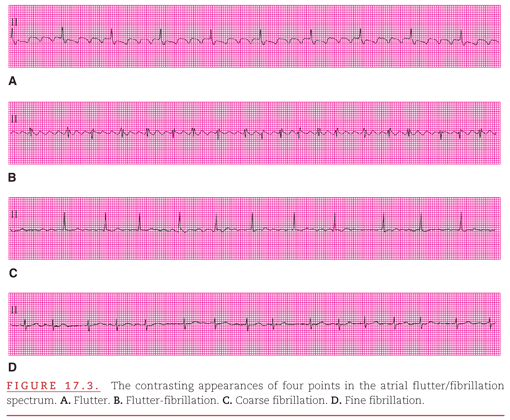
Reentrant Atrial Tachyarrhythmias The Atrial Flutter Fibrillation Spectrum Thoracic Key
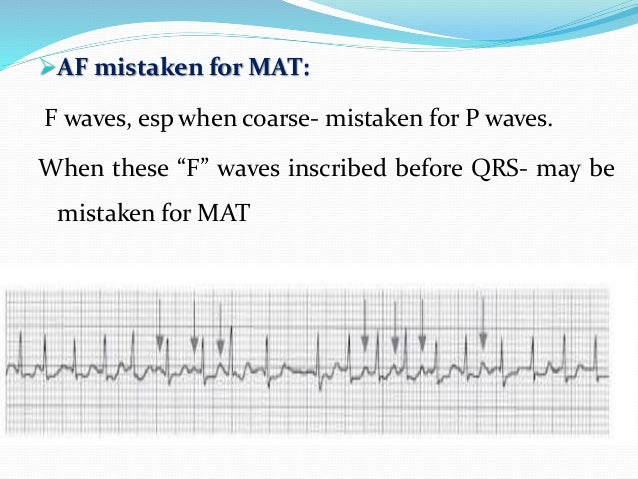
Atrial Fibrillation

Atrial Fibrillation

Separating Atrial Flutter From Atrial Fibrillation With Apparent Electrocardiographic Organization Using Dominant And Narrow F Wave Spectra Sciencedirect
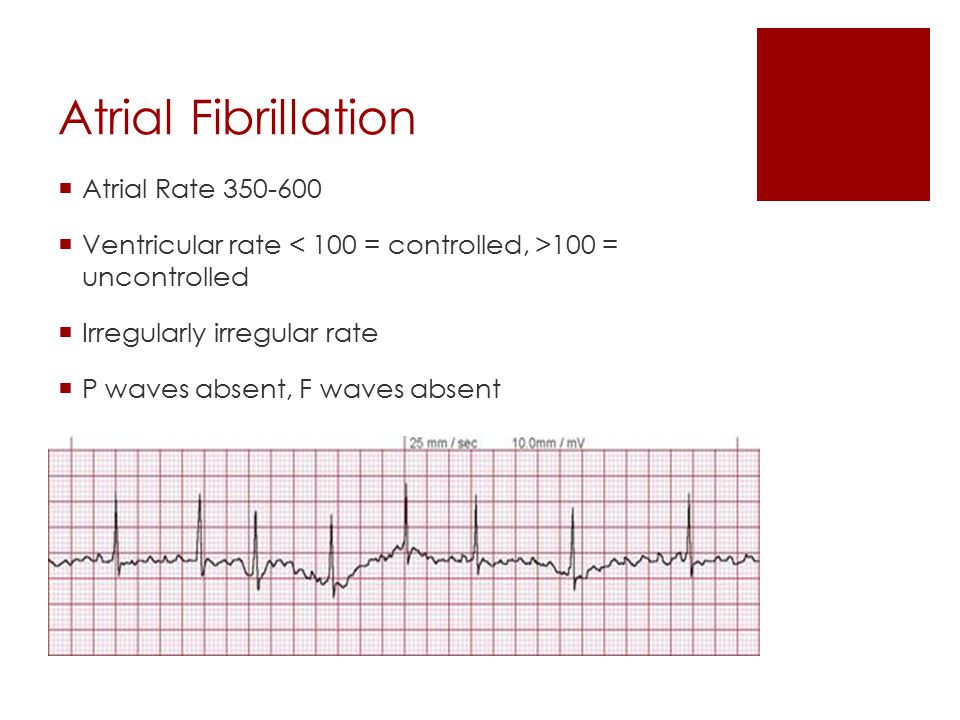
Cardiac Dysrhythmias Nuro 438 February Ppt Video Online Download
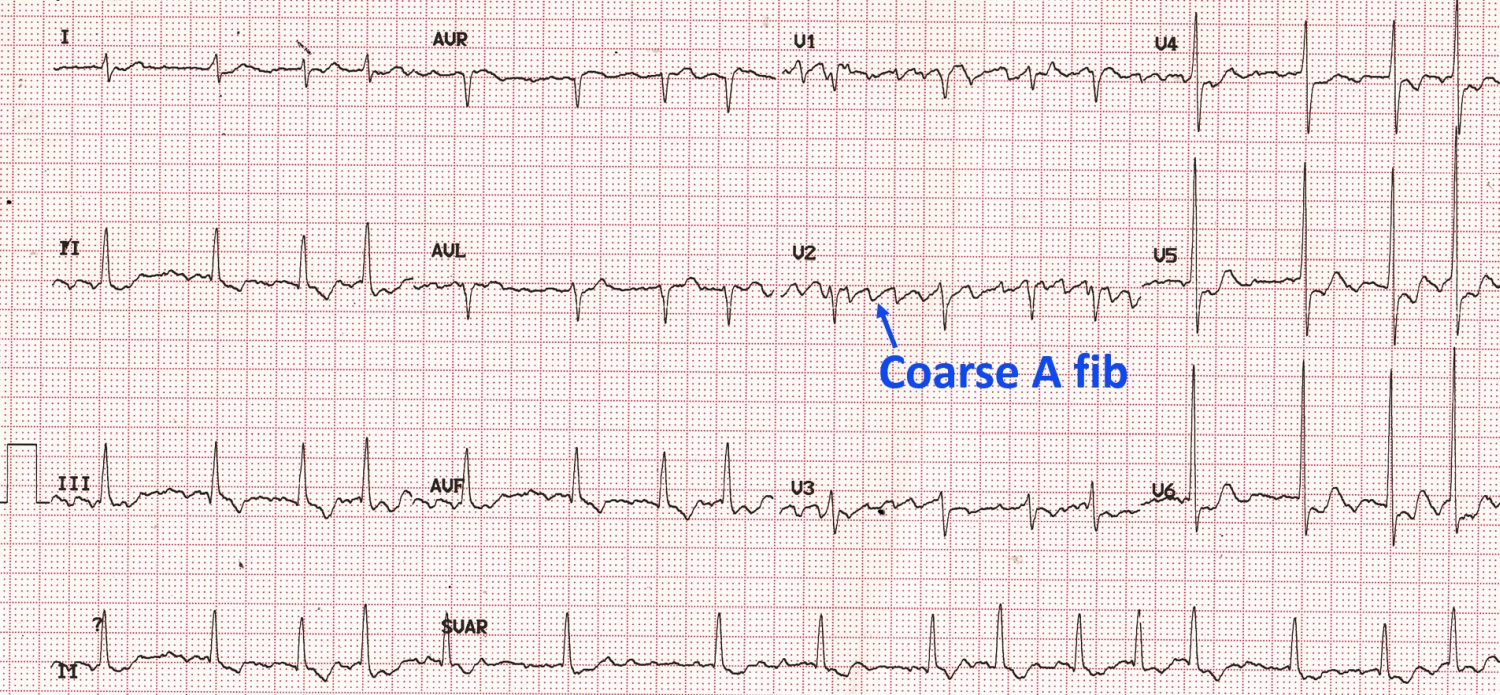
Coarse Atrial Fibrillation On Ecg All About Cardiovascular System And Disorders

Atrial Fibrillation Af Atriyal Fibrilasyon Ekg Ecg Ankara Kardiyoloji Kalp Hastaliklari Mete Alpaslan Doktorekg Com
Nursing Management Dysrhythmias Nurse Key

Figure 1 From Acute Management Of Atrial Fibrillation Part I Rate And Rhythm Control Semantic Scholar
Atrial Fibrillation Thoracic Key

Figure 3 From Atrial Fibrillation Semantic Scholar
Atrial Flutter Wikipedia
Atrial Fibrillation Litfl Medical Blog Ecg Library Diagnosis

Atrial Fibrillation Good

The 12 Rhythms Of Christmas Atrial Flutter Ems 12 Lead

Chapter 3 Supraventricular Rhythms Ii Atrial Fibrillation Ppt Download
Atrial Flutter Classification Causes Ecg Diagnosis Management Ecg Echo
1

What Is The Difference Between Atrial Fibrillation A Fib Atrial Flutter A Flutter
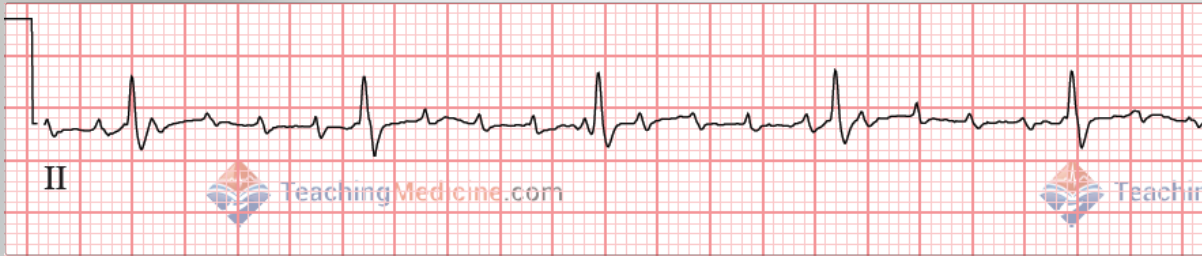
Lesson Title Atrial Flutter

Lesson Title Atrial Flutter
Atrial Flutter Classification Causes Ecg Diagnosis Management Ecg Echo

What Is The Difference Between Atrial Fibrillation A Fib Atrial Flutter A Flutter

Separating Atrial Flutter From Atrial Fibrillation With Apparent Electrocardiographic Organization Using Dominant And Narrow F Wave Spectra Sciencedirect

Atrial Flutter Is A Type Of Atrial Los Angeles Echo Society Facebook
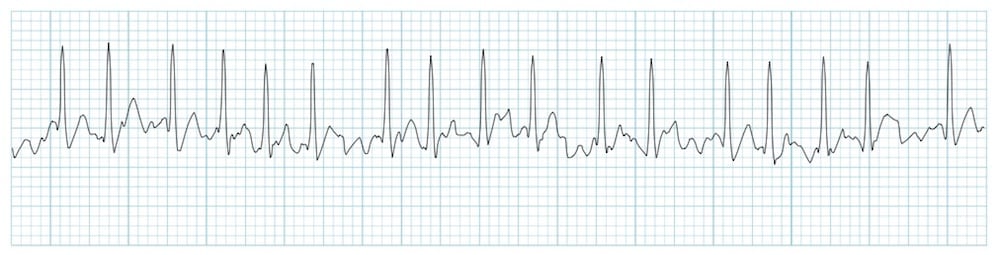
Atrial Fibrillation Litfl Medical Blog Ecg Library Diagnosis

The 12 Rhythms Of Christmas Atrial Flutter Ems 12 Lead

Pdf Atrial Fibrillation And Waveform Characterization
Q Tbn 3aand9gcrudpyslo afcjdv9bvkvfgobme3zjzz3rglekumrjllipvkk Usqp Cau
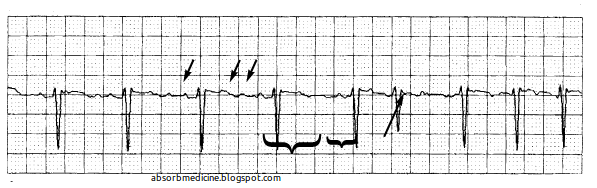
Absorb Medicine Management Of Atrial Fibrillation Af

Ecg Showing Atrial Fibrillation Note Varying Rr Intervals No Discrete Download Scientific Diagram
3
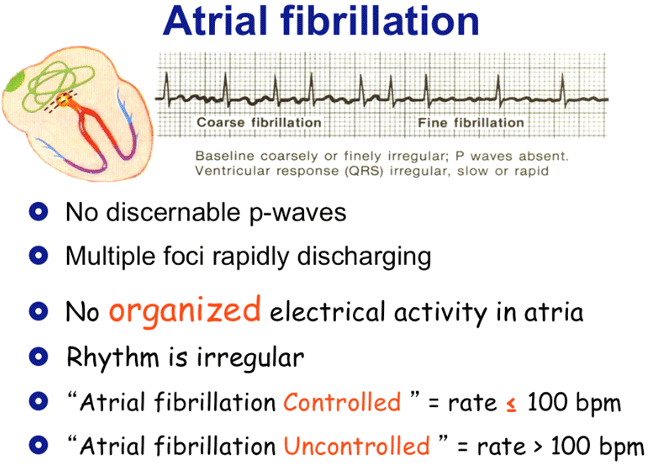
Atrial Flutter And Atrial Fibrillation

Non Invasive Prediction Of Catheter Ablation Outcome In Persistent Atrial Fibrillation By Fibrillatory Wave Amplitude Computation In Multiple Electrocardiogram Leads Sciencedirect

Pdf Atrial Fibrillation And Waveform Characterization
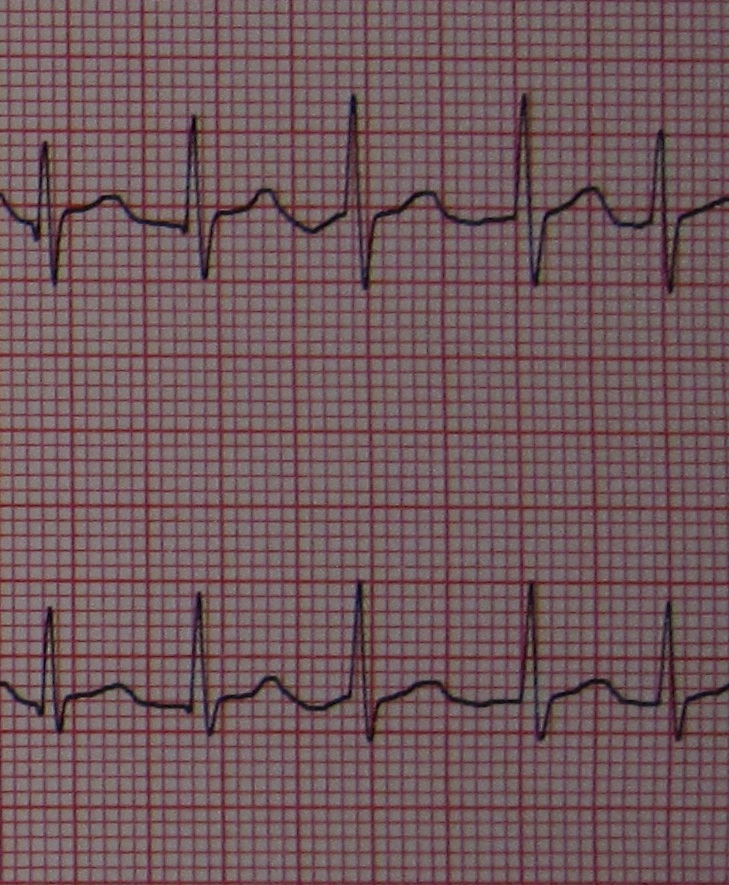
Atrial Fibrillation Wikipedia

Supraventricular Arrhythmias Part 2 Cardiac Rhythm Disturbances Clinical Electrocardiography A Simplified Approach 7th Edition 06
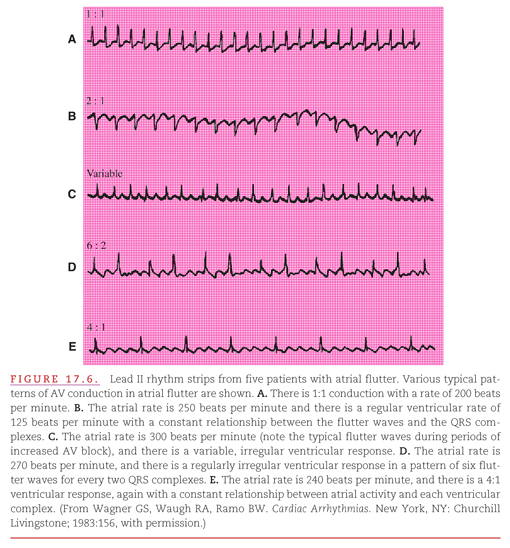
Reentrant Atrial Tachyarrhythmias The Atrial Flutter Fibrillation Spectrum Thoracic Key
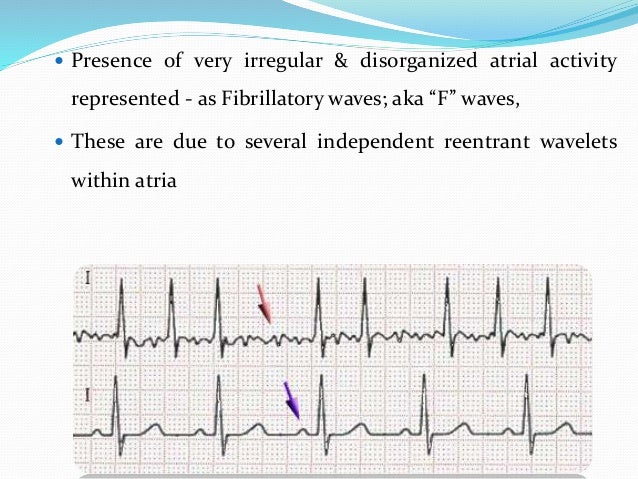
Atrial Fibrillation
Ppt Atrial Fibrillation Rhythm Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id

Figure 3 From Ladder Diagrams For Atrial Flutter And Atrial Fibrillation Semantic Scholar

Atrial Fibrillation P Waves Are Absent F Waves With A Variable Download Scientific Diagram
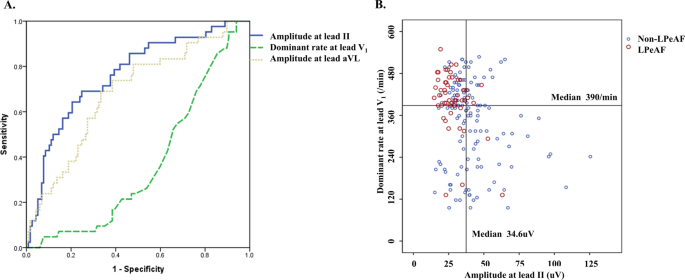
Early Differentiation Of Long Standing Persistent Atrial Fibrillation Using The Characteristics Of Fibrillatory Waves In Surface Ecg Multi Leads Scientific Reports
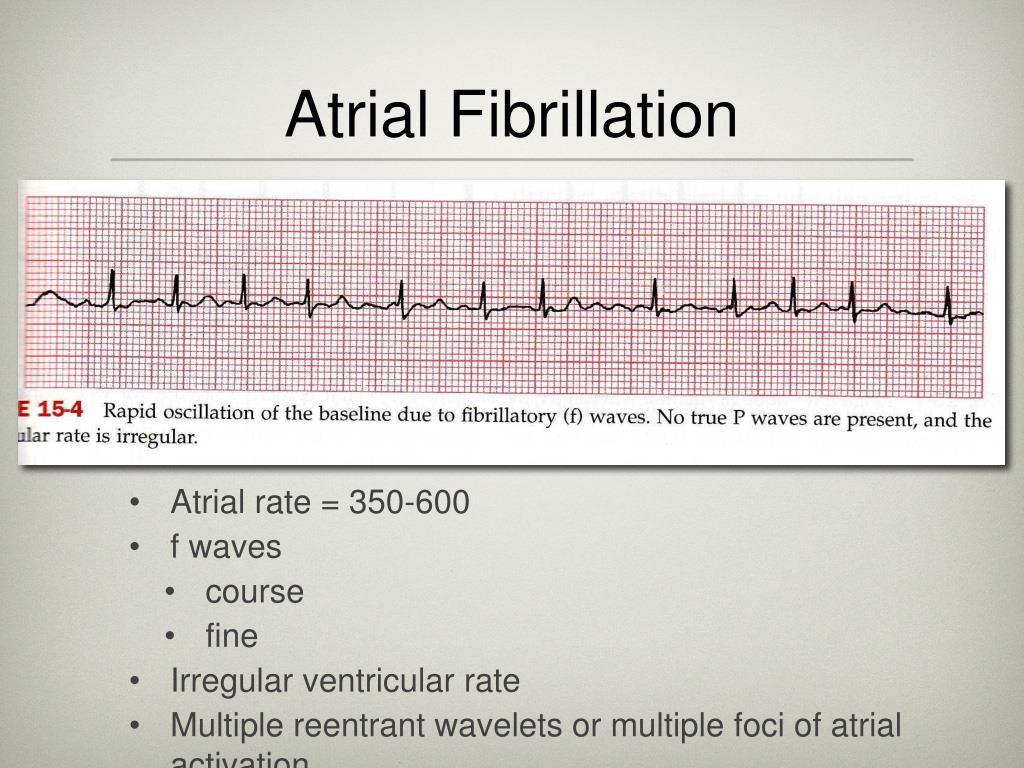
Ppt Atrial Flutter And Atrial Fibrillation Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
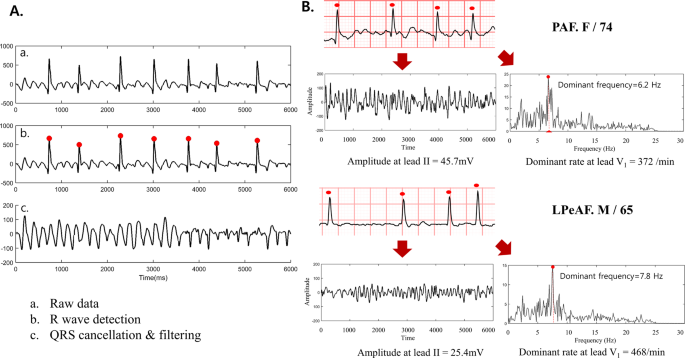
Early Differentiation Of Long Standing Persistent Atrial Fibrillation Using The Characteristics Of Fibrillatory Waves In Surface Ecg Multi Leads Scientific Reports
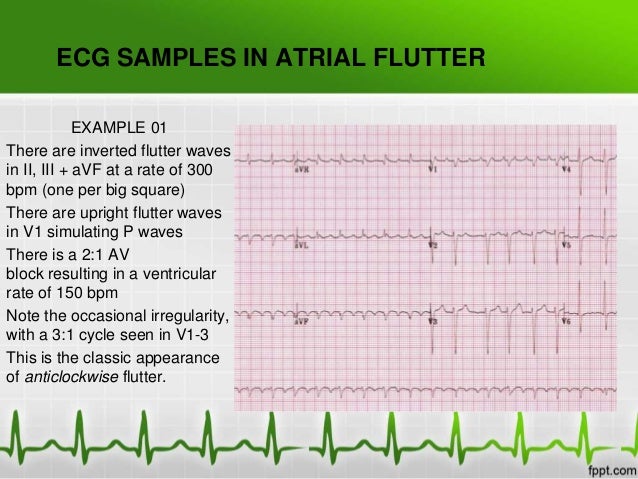
Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter

Atrial Fibrillation Definition Of Atrial Fibrillation By Medical Dictionary

Perioperative Management Of Atrial Fibrillation Ppt Video Online Download
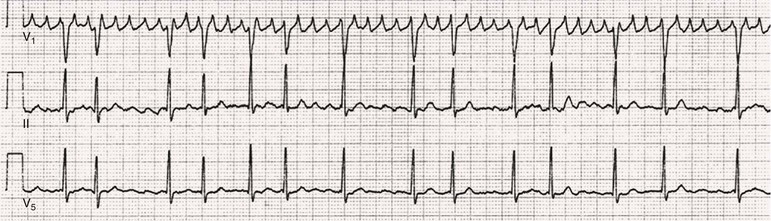
Atrial Fibrillation Thoracic Key
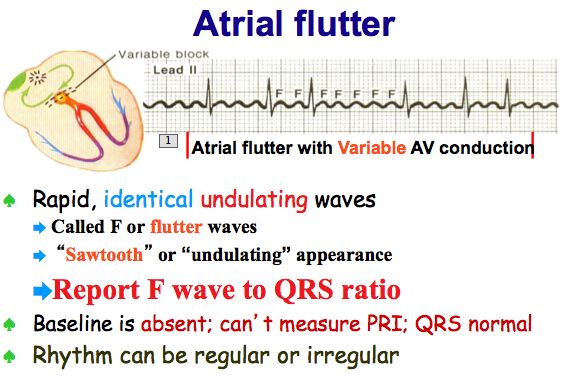
Atrial Flutter And Atrial Fibrillation
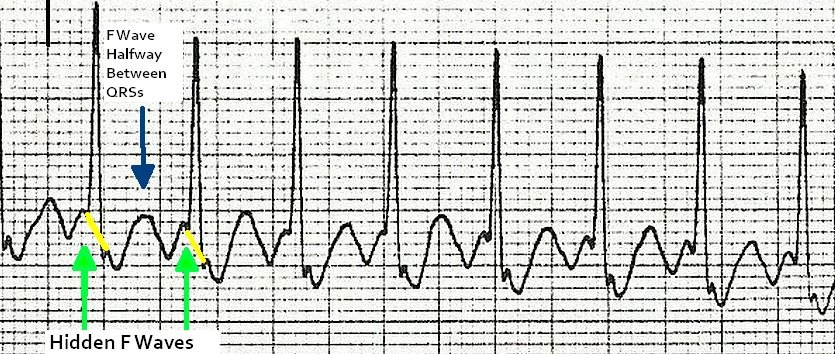
10 Tips To Never Miss Atrial Flutter With 2 1 Conduction
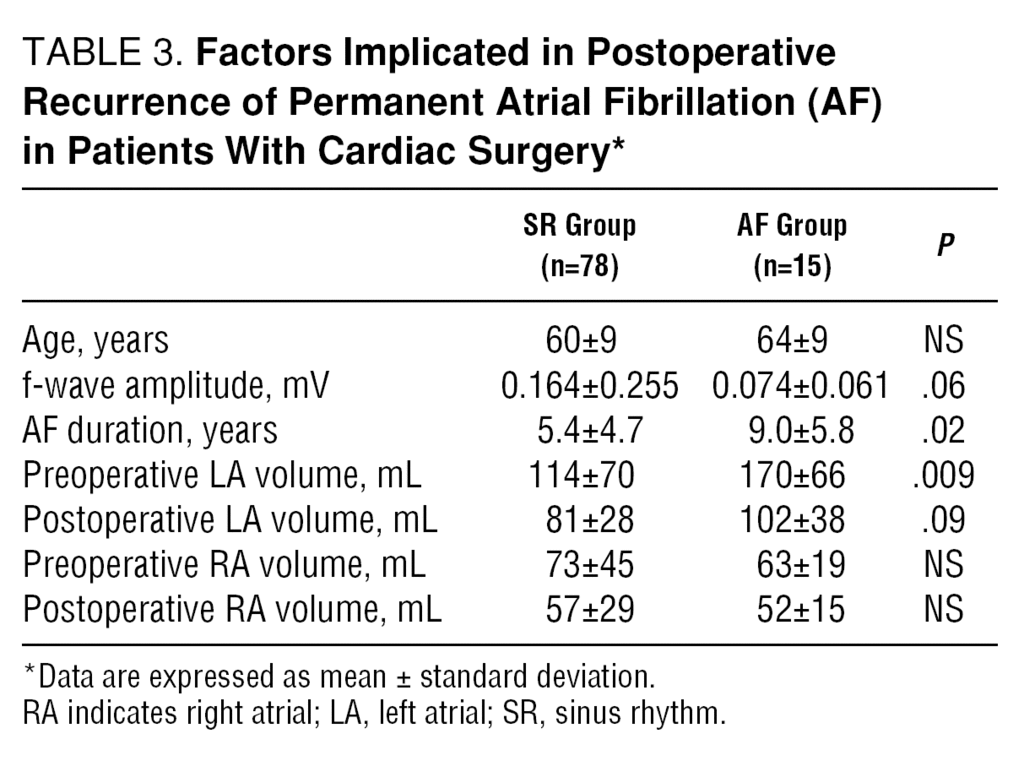
Ablation Of Permanent Atrial Fibrillation In Cardiac Surgery Short Term And Mid Term Results Revista Espanola De Cardiologia English Edition

Pdf F Wave Amplitude Stability On Multiple Electrocardiogram Leads In Atrial Fibrillation
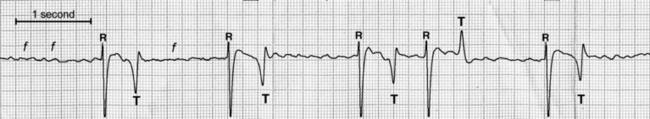
Management Of Atrial Fibrillation Veterian Key

Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter

Pin On Atrial Flutter

Pdf The Diagnosis And Management Of Atrial Fibrillation In The Horse
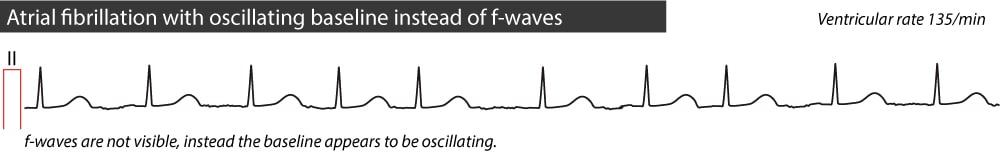
Atrial Fibrillation Ecg Classification Causes Risk Factors Management Ecg Echo

Ati Med Surg I Cardiac Issues Dysrhythmias Cardiac Monitoring Pacemakers Inflammatory Cardiac Disorders Ekg Review Angina And Mi Heart Failure And Pulmonary Edema Flashcards Quizlet
Ieeexplore Ieee Org Iel7 Pdf
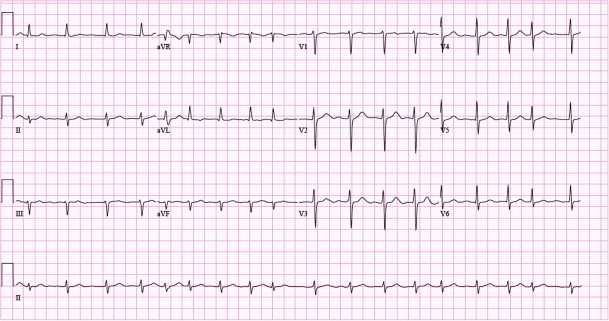
Atrial Fibrillation Ecg Classification Causes Risk Factors Management Ecg Echo

Lesson Title Atrial Flutter

Atrial Fibrillation Good
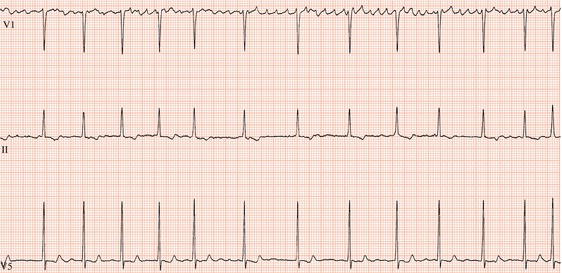
Atrial Fibrillation Thoracic Key
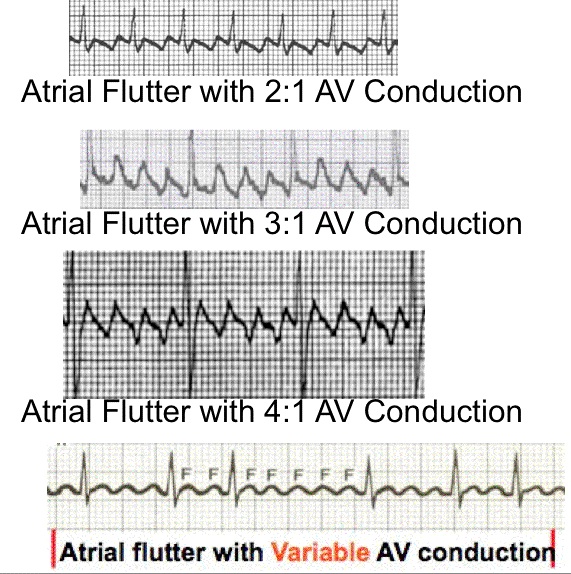
Atrial Flutter And Atrial Fibrillation

Atrial Fibrillation Wikipedia
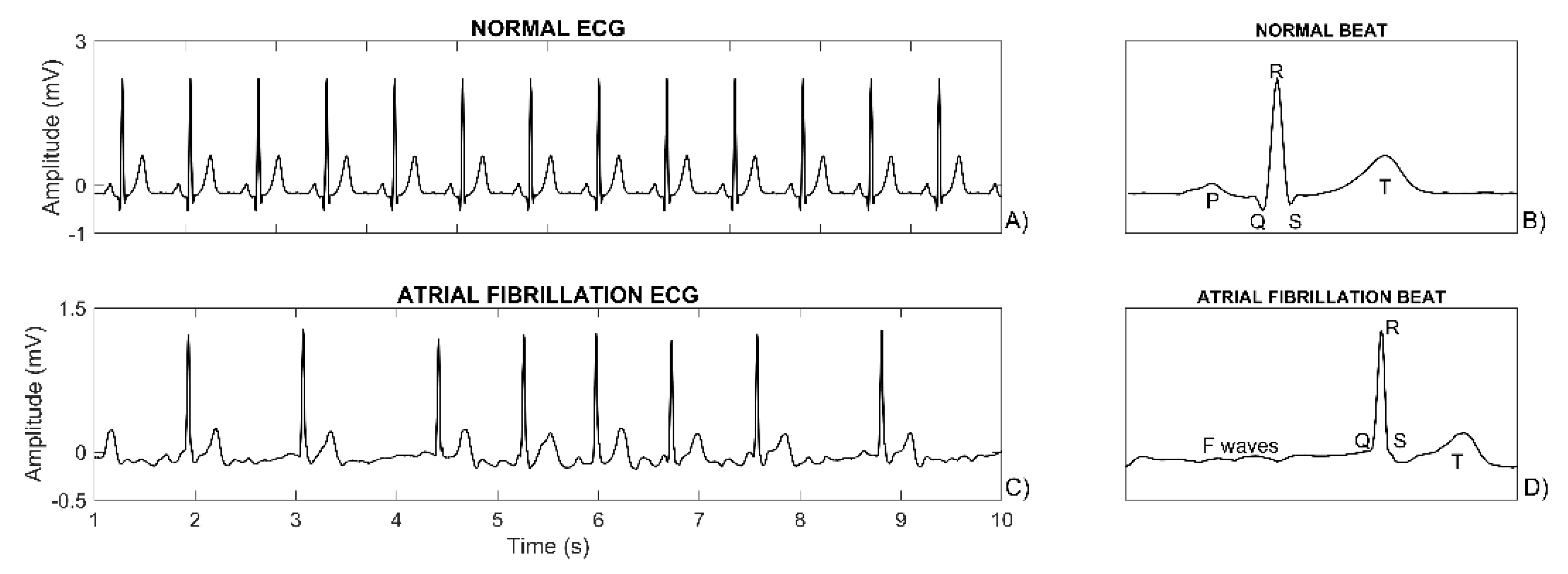
Sensors Free Full Text Artificial Neural Network For Atrial Fibrillation Identification In Portable Devices Html

Pdf Intracardiac Overdrive Pacing As A Treatment Of Atrial Flutter In A Horse
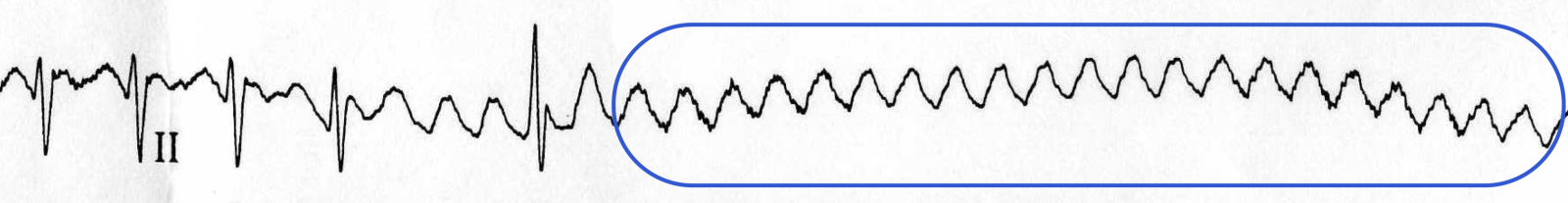
Lesson Title Atrial Flutter

What Does Af Look Like Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Fibrillation And Flutter Cardiology Teaching Package Practice Learning Division Of Nursing The University Of Nottingham

Atrial Fibrillation Ecg Of A 62 Year Woman Clear Irregular Irregular Download Scientific Diagram
Cardiac Arrhythmias Online Presentation

Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader

During Atrial Fibrillation Intra Atrial Waves Are Completely Chaotic Download Scientific Diagram

Atrial Fibrillation Good



